Yolande de Dreux was Scotland’s Queen Consort for only 4 months and 14 days. In that short time, she carried the hope of a nation – and its king – to secure the Scottish succession.
Yolande was born into a cadet branch of the French royal family, probably sometime in the mid-1260s. Her father was Robert IV, Count of Dreux, who died in 1282 and her mother was Beatrice de Montfort, who died in 1311. Beatrice was the daughter of Count Jean I de Montfort l’Amoury and his wife Jeanne de Chateaudun, Beatrice was therefore a great-granddaughter of Simon de Montfort, earl of Leicester, and heiress to the impressive de Montfort estates. One of 6 children, Yolande had 2 brothers and 3 sisters. Little is known of Yolande’s childhood but we can imagine that as a junior member of the Capetian dynasty, she grew up amidst some privilege and splendour.
Whilst Yolande was growing into adulthood Scotland was experiencing a “golden age”, a period of relative peace and prosperity. Her king, Alexander III was married to Margaret, daughter of Henry III of England and the couple had 3 children survive childhood. Their daughter, Margaret, born at Windsor on 28th February, 1261, was married to Erik II, king of Norway, in August 1281. Their eldest son, Alexander, was born on 21st January 1264, at Jedburgh. On 15th November 1282 Alexander married Margaret, the daughter of Guy de Dampierre, Count of Flanders. A younger son, David was born on 20th March 1273.
Queen Margaret died in 1275 and within 8 years all 3 of her children were dead; 8-year-old David died at Stirling Castle at the end of June 1281, Margaret died in childbirth on 9th April 1283 and Alexander died at Lindores Abbey in January 1284, sometime around his 20th birthday. Alexander’s heir was now his infant granddaughter by Margaret and Erik, little Margaret, the Maid of Norway, born shortly before her mother’s death.
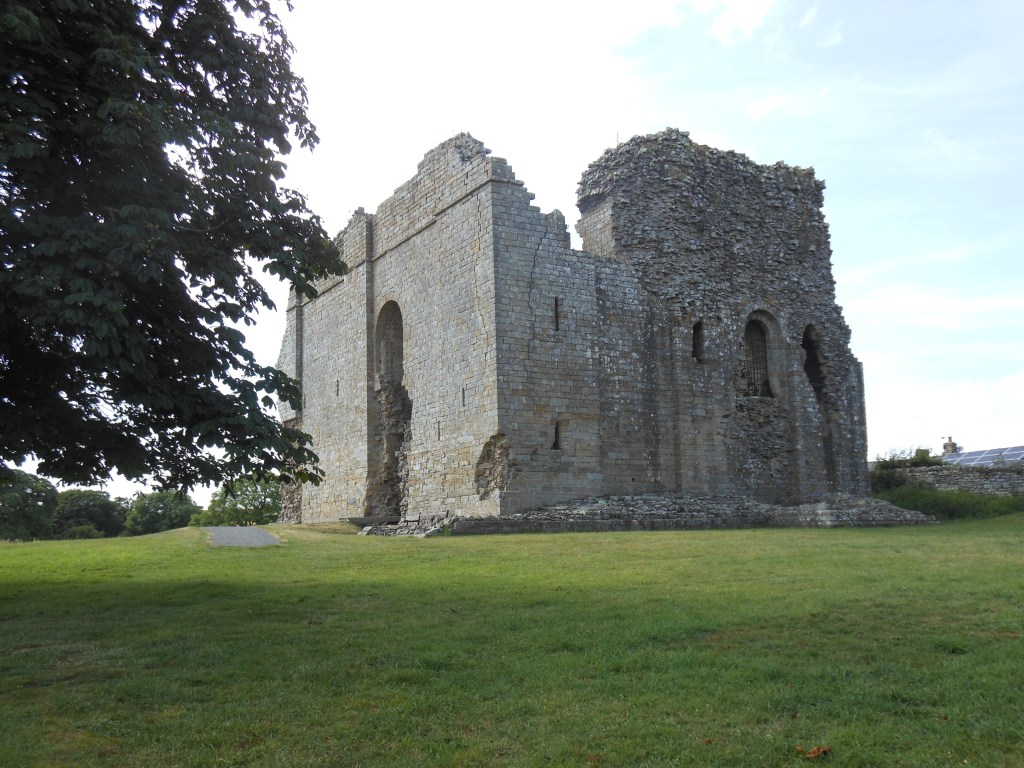
With his entire dynasty resting on the life of his toddler granddaughter, Alexander started the search for a new wife. In February 1285 he sent a Scottish embassy to France for this sole purpose. Their successful search saw Yolande arrive in Scotland that same summer, accompanied by her brother John. Alexander and Yolande were married at Jedburgh Abbey, Roxburghshire, on 14th October 1285, the feast of St Calixtus, in front of a large congregation made up of Scottish and French nobles. Yolande was probably no more than 22 years of age, while Alexander was in his 44th year.
The marriage was one of the shortest in British royal history – and the shortest of any English or Scottish king, lasting less than 5 months. Tragedy struck on 19 March 1286.
Alexander had spent the day attending a council meeting in Edinburgh. When the meeting broke up he set off on horseback to join his wife at Kinghorn Castle in Fife. It was said he wanted to be there to celebrate her birthday and he may also have recently discovered that she was pregnant with the much-desired heir. For whatever the reason, he was eager to get to her and took only a small escort of 3 men and 2 local guides. It seems that, with bad weather closing in and daylight fading, several people counselled against continuing the journey, including the ferryman at the River Forth and the bailie at Inverkeithing, who argued that Alexander should stay the night and continue his journey in the morning as a heavy storm was brewing.
Only 8 miles from his destination, Alexander would hear none of it and insisted on continuing his journey. He somehow lost his escort in the dark and worsening weather, but continued alone. It was the next morning when his body was found on the foreshore of Pettycur, just a mile from his destination. The most likely explanation was that his horse had stumbled, throwing the king whose neck was broken in the fall, although at least one historical fiction writer has suggested foul play while others have suggested the king was drunk.
There followed months of uncertainty in Scotland. She had lost one of her most successful kings and the succession was in turmoil. Little Margaret, the Maid of Norway, had been recognised by the council as Alexander’s heir, but his queen was pregnant; and if she gave birth to a boy he would be king from his first breath. A regency council was established to rule until the queen gave birth.
In the event, Yolande either suffered a miscarriage, or the child was stillborn. Some sources, the Lanercost Chronicle in particular, have questioned whether Yolande was pregnant at all, suggesting that she was intending to pass off another woman’s baby as her own. The plan thwarted, the chronicle recorded that ‘women’s cunning always turns toward a wretched outcome‘.¹ However, there are major discrepancies in the chronicle’s apparently malicious account and tradition has the baby buried at Cambuskenneth.
The throne passed to little Margaret and arrangements began to have her brought to England, with marriage negotiations being opened with Edward I for the little queen to marry his son and heir; the future Edward II. Yolande continued to reside in Scotland for some time, possibly at Stirling Castle, and was confirmed in her dower properties, which included an annual income of £200 from Berwick; she also had estates in the sheriffdom of Stirling and a horse stud at Jedworth.
Margaret’s death at sea in 1290, while on her journey to her new kingdom, threw Scotland into years of turmoil, with 13 nobles advancing their competing claims to the crown and Edward I of England claiming the right to choose Alexander III’s successor, and recognition as Scotland’s overlord. The English king’s imperialist ambitions had thrown Scotland into crisis by 1296.
Luckily for Yolande, she was already far away from Scotland and the brewing wars. In May 1294 Yolande had married for a second time; Arthur of Brittany was a similar age to Yolande and was the son and heir of Jean II, duke of Brittany and earl of Richmond. Yolande was the second wife of Arthur, who already had 3 sons, Jean, Guy and Peter, by his first wife, Marie, Vicomtesse de Limoges.
It is possible that Arthur chose Yolande as a bride due to the impressive de Montfort territories that she stood to inherit from her mother, although there were legal wranglings between Yolande and her younger sister, Jeanne, who also claimed the lands.
Yolande and Arthur had 6 children together. Their eldest daughter, Joan was born a year after their marriage and married Robert, Lord of Cassel; she died in 1363. Beatrice was born c.1295 and married Guy, Lord of Laval; she lived until 1384. Their only son, John, was probably born 1295/6 and married Joan of Flanders. Of the 3 youngest daughters: Alice was born in the late 1290s married Bouchard VI, Count of Vendôme and died in 1377; Blanche was born in 1300 and died young; Mary was born in 1302 and became a nun, she died in 1377.
Arthur succeeded his father as Duke of Brittany in 1305 and ruled until his death in 1312. He was succeeded by John III, his eldest son by his first marriage. However, John’s death in 1341 sparked the War of the Breton Succession when Yolande’s son, John de Montfort, claimed the duchy in place of Joan of Penthièvre, daughter of Guy (Arthur’s 2nd son by his 1st wife), who was married to Charles of Blois, nephew of King Philip VI of France. Joan and Charles were therefore backed by the French crown, and Edward III of England supported the claims of John de Montfort; the war eventually became part of the greater conflict, the Hundred Years War. When John fell ill and died in 1345, the war continued in the name of his 6-year-old son and Yolande’s grandson, another John (John IV, duke of Brittany) and finally ended in John’s favour with the treaty of Guérande in April 1365.
After being widowed for a second time Yolande did not remarry.
During her time in Brittany Yolande continued to administer to her Scottish estates; in October 1323 safe-conduct to Scotland was granted to a French knight ‘for the dower of the Duchess of Brittany while she was Queen of Scotland‘.² It seems uncertain when Yolande died. Sources vary between 1324 and 1330, although she was still alive on 1st February 1324 when she made provision for the support of her daughter, Marie, who had become a nun.
These arrangements for her daughter are the last mention of Yolande in the historical record, the date of her death as uncertain as that of her birth.
*
Footnotes: ¹ Chronique de Lanercost, 118, quoted by Jessica Nelson in Oxforddnb.com. ²CSP Scot.. 3. no. 829 quoted by Jessica Nelson in Oxforddnb.com.
*
Pictures courtesy of Wikipedia, except Jedburgh Abbey, which is ©2016 Sharon Bennett Connolly.
*
Sources: Marc Morris Edward I: A Great and Terrible King by Marc Morris; Brewer’s British Royalty by David Williamson; The Mammoth Book of British kings & Queens by Mike Ashley; Britain’s Royal Families by Alison Weir; The Oxford Companion to British History edited by John Cannon; The History Today Companion to British History Edited by Juliet Gardiner and Neil Wenborn; The Story of Scotland by Nigel Tranter; Scotland, History of a Nation by David Ross; oxforddnb.com; undiscoveredscotland.co.uk; freelancehistorywriter.com.
*
My books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell and Michael Jecks, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved. Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2016 Sharon Bennett Connolly, FRHistS