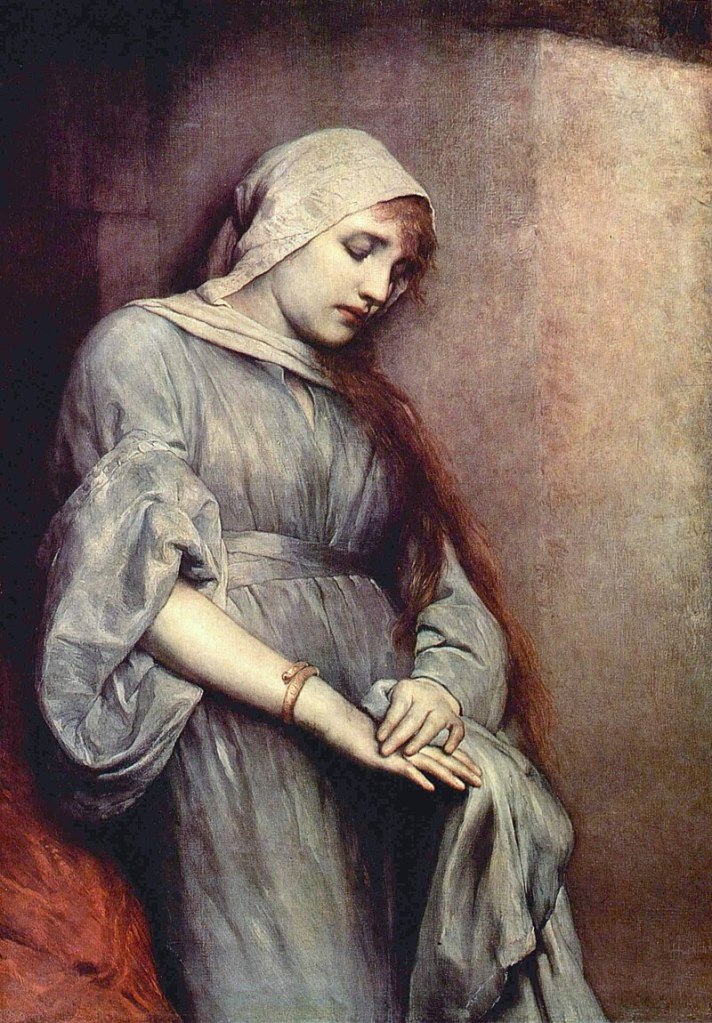
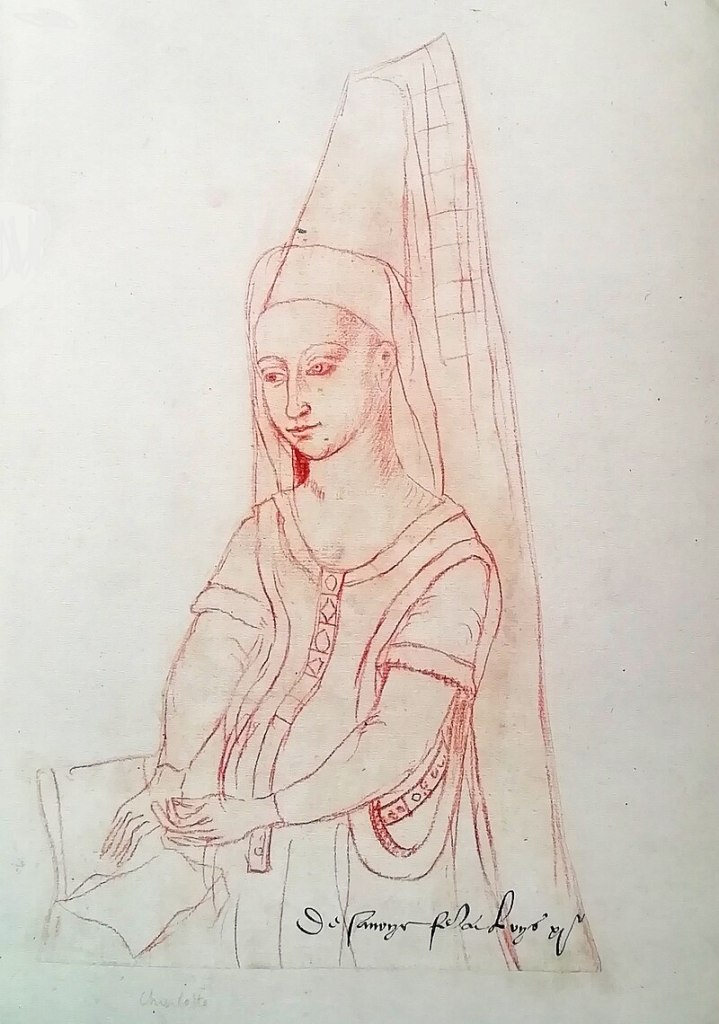
You may have noticed that I love the stories of women from medieval times who do the remarkable, who will defy a tyrant or hold a castle while under siege. Women like Nicholaa de la Haye. And yet, Nicholaa was not the only medieval woman to hold tenaciously to a castle under siege. It was more common than one might think. Matilda de Braose (or Briouze), the Lady of Hay, was another such, who held her castle against the besieging Welsh; as was Agnes of Dunbar, known to history as Black Agnes and a woman who was a blight on English forces in Scotland. Agnes was a bold lady whose acts of defiance against the English would surely have impressed Nicholaa, nationalities aside, of course.
Agnes was the eldest daughter of Thomas Randolph, 1st Earl of Moray, and his wife Isabel, a daughter of Sir John Stewart of Bunkle. Thomas Randolph was a favoured nephew of Robert the Bruce, King of Scots, and one of his most stalwart supporters. Randolph was rewarded with the earldom of Moray and the appointment as guardian during the minority of King Robert’s son and successor, David II, in 1329.
There is very little known of the early life of Agnes, until about 1320, when she was married to Patrick, Earl of Dunbar. We can imagine that Agnes envisioned a life as a typical laird’s lady, raising children, looking after the land and tenants while her husband was away fighting. Unfortunately, Agnes and Patrick would remain childless, so the countess was not preoccupied with raising children. Agnes’s younger sister, Isabel, was married to Sir Patrick Dunbar, Earl Patrick’s cousin, and it would be their son, George, who would be made heir to Earl Patrick and Agnes.
From the timing of the marriage, we can surmise that Agnes was probably born just after the turn of the century, into a country struggling to gain independence from its aggressive neighbour, England. It would, therefore, not be unreasonable to assume that she saw little of her father during her early years as he was frequently away fighting; even after the Scottish victory at Bannockburn in 1314, Randolph continued in active service for the Scottish crown, fighting with Robert the Bruce in Ireland in 1317, and in the borders with England in 1318 and 1319.
Scotland’s troubles continued long into the reign of David II, with the English backing David’s rival, Edward Balliol, son of Scotland’s former king, John Balliol. This despite David II being married to Edward III’s sister, Joan of the Tower. The throne would pass back and forth between the two claimants for several years. When Agnes’s father died in 1332, he was succeeded by her brother Thomas, who was killed just weeks later, at the Battle of Dupplin Moor, fighting those who had been disinherited during the Wars of Independence. Thomas, in turn, was succeeded by another brother, John, who was killed fighting the English at the Battle of Neville’s Cross in 1346.
On John’s death, the earldom of Moray would pass to Agnes’s husband in right of his wife. Agnes and Patrick were cousins within the prohibited degree of consanguinity and a dispensation had been needed for them to marry. According to the chronicler, Pitscottie, she gained her name of Black Agnes ‘be ressone she was blak skynnit’, suggesting Agnes had a dark complexion; her black hair, dark eyes and olive skin more common among Mediterranean countries than the northern fastness of Scotland.1 The English attributed a different reason to her name, to them, Black Agnes was the most evil Scotswoman who ever lived. Pitscottie went on to say of Agnes that she was ‘of greater spirit than it became a woman to be’, which, given her actions in the face of the enemy, is a fair appraisal of an incredible woman.2
Agnes was not the only woman to become heavily involved in the Scottish Wars of Independence, which had been a different kind of war from the very beginning. Robert the Bruce’s wife, daughter and sisters had been imprisoned for eight years by Edward I; his sister Christian would herself become involved in the fighting during her nephew David’s reign, defending the castle of Kildrummy against the supporters of Edward Balliol, in 1335.
Most of Agnes Randolph’s life is shrouded in mystery; there is very little mention of her existence until the English army appeared before her castle of Dunbar in January 1338. With the resumption of hostilities between England and Scotland in the 1330s, the castle of Dunbar became strategically important for both sides.
The stronghold had been rebuilt, at the expense of Edward III, in 1333, but by 1337 it was standing against England’s king. English affairs in the north lay in the hands of Richard (II) FitzAlan, Earl of Arundel, and William Montague, Earl of Salisbury, and it was these two experienced military leaders who decided to launch an English offensive by attacking Dunbar. An impressive stronghold, the castle was all but impregnable; it was built at the mouth of the Dunbar harbour, on separate rocks, with interlinking bridges and corridors.
Strategically, the castle’s position made it impossible for the English to march past it and leave it behind them, intact, able to harry the invaders and cut their lines of communication with England. Earl Patrick was away from home at the time, however, Scottish writer Nigel Tranter suggests that Agnes deliberately allowed herself to be besieged to give the Scottish forces time to rally and organise a resistance to the English invasion. Even so, it must have been a terrifying sight for the countess to look out from the battlements and see an army approaching; and the English earls must surely have been confident that they could beat the countess and her reduced garrison.
In January 1338, the English laid siege to Dunbar, surrounding it as best they could. The army had brought a legion of engineers with it, thus ensuring that a vast number of siege engines could be constructed and the castle’s inhabitants would face an almost constant barrage from missiles. When Salisbury demanded that Agnes surrender, she is said to have responded,
Of Scotland’s King I haud my House,
He pays me meat and fee,
And I will keep my gude and house,
While my house will keep me.3
The siege didn’t go exactly as the English planned. Agnes mocked them at every opportunity, appearing on the battlements even during bombardments. She is said to have had her maids dusting the battlements where they had been struck by missiles. When a siege engine known as a sow (a battering ram) was brought to face the castle, Agnes is said to have taunted the English by shouting ‘Beware, Montagow, for fallow shall they sow.’ The Scots would use the displaced rocks, caused by the barrages, and the missiles that had been fired at them, and rain them back down on their enemies. As the sow was destroyed and the English took cover, Agnes is said to have shouted ‘Behold the litter of English pigs.’4 Attack after attack was repulsed by Agnes and her men; a ballad, said to have been written by Salisbury himself, demonstrates Agnes’ steadfast attitude:
She makes a stir in tower and trench,
That brawling, boisterous, Scottish wench;
Came I early, came I late,
I found Agnes at the gate!5
The English even tried subterfuge to win the castle, bribing one of the castle’s guards to raise the gate and allow entry to the English attackers. However, the guard, having taken the money, went straight to Agnes:
Believing that they were going to be entering the castle, the Earl and his soldiers arrived at the gate. The guards, thinking Salisbury would be first to enter, dropped the gate after the first soldier stepped into the castle. Fortunately for Salisbury, one of his men had passed him on the approach. The thwarted earl retreated back to his camp with Agnes yelling at him from the castle walls: ‘Fare thee well Montague, I meant that you should have supped with us and support us in upholding the castle from the English!’5
At one point, the English used Agnes’s brother John Randolph in an attempt to persuade her to submit. One of the regents of Scotland during David II’s minority, John had been ambushed and captured in 1335. He was brought before Dunbar Castle, where Salisbury threatened to hang him in full view of his sister. Unperturbed, Agnes responded that John’s death could only be to her own benefit; although she could not inherit John’s titles, she was, alongside her sister, co-heir to his lands. John was given a reprieve and sent to imprisonment in England. Ironically, he would be freed in 1341 as part of a prisoner exchange; for the earl of Salisbury, of all people!
The problem for the English lay in the fact that they could not entirely surround the castle. Although they could besiege it from the land, the castle was still accessible by sea. An English fleet was guarding the harbour, but Sir Alexander Ramsay of Dalhousie managed to replenish the castle’s dwindling supplies by using a fleet of fishing boats, approaching in the early dawn from the cover of the Bass Rock. He managed to sneak through the enemy lines, making a dash for the harbour before the larger English vessels could get underway. Ramsay managed to land vital supplies and reinforcements for the garrison through a partially submerged entrance.
Agnes even sent the Earl of Salisbury some fresh-baked food when she knew the English supplies were running low, taunting the poor earl. Eventually, Agnes’s resistance proved too much for the English army, and, after nineteen weeks, on 10 June 1338, they lifted the siege, claiming their men and resources were needed for the king’s campaigns overseas. It had cost over £6,000, prompting one English chronicler to record that the siege had been ‘wasteful, and neither honourable nor secure, but useful and advantageous to the Scots’.6
The struggle against the English continued for several more years, but David II and his queen, Joan of the Tower, the daughter of Edward II and sister of Edward III, returned to Scotland amid great rejoicing in 1341; only for David to become a captive of Edward III following the Battle of Neville’s Cross in 1346. Scotland’s king spent eleven years in English captivity, while Scotland was ruled by his nephew and heir, Robert the Steward.
David returned in 1357, the same year that Patrick, Earl of Dunbar, participated in the raid that saw Berwick returned to Scottish sovereignty, for a short time at least. Earl Patrick continued to witness royal charters until July 1368 and remained active in Scottish affairs until his death in 1369. When Agnes also died in 1369, aged about 57, her father’s earldom and that of her husband passed to her nephew, George Dunbar.
Agnes of Dunbar was a women of status, raised to command households, if not men, who stepped up to the mark when the occasion demanded it. Although she was not educated in military techniques and tactics, she had lived within a world that was constantly on a war footing and when faced with a fight, she rose to the challenge. With her death, Black Agnes passed into legend, her tenacity and stalwart defence of Dunbar Castle a shining example of what a mere woman can be capable of achieving.
Images:
Courtesy of Wikipedia
Notes:
1. The historie and cronicles of Scotland … by Robert Lindesay of Pitscottie, ed. A. J. G. Mackay, 3 vols, Scottish Text Society, 42–3, 60 (1899–1911); 2. ibid; 3. Kyra Cornelius Kramer, Black Agnes and Psychological Warfare, kyrackramer.com; 4. Nigel Tranter, The Story of Scotland; 5. Kramer, Black Agnes and Psychological Warfare; 6. Historia Anglicana
Sources:
The historie and cronicles of Scotland … by Robert Lindesay of Pitscottie, ed. A. J. G. Mackay, 3 vols, Scottish Text Society, 42–3, 60 (1899–1911); Kyra Cornelius Kramer, Black Agnes and Psychological Warfare, kyrackramer.com; Nigel Tranter, The Story of Scotland; oxforddnb.com; Brewer’s British Royalty by David Williamson; Kings & Queens of Britain by Joyce Marlow; Mammoth Book of British Kings & Queens by Mike Ashley; Oxford Companion to British History Edited by John Cannon; Britain’s Royal Families by Alison Weir; educationscotland.gov.uk/scotlandhistory; englishmonarchs.co.uk; The Perfect King by Ian Mortimer; Scotland, History of a Nation by David Ross; The Life & Times of Edward III by Paul Johnson; The Reign of Edward III by W.M. Ormrod
*
My Books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online bookshop.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
‘Scotland’s Medieval Queens gives a thorough grounding in the history of the women who ruled Scotland at the side of its kings, often in the shadows, but just as interesting in their lives beyond the spotlight. It’s not a subject that has been widely covered, and Sharon is a pioneer in bringing that information into accessible history.’ Elizabeth Chadwick (New York Times bestselling author)
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Coming 30 March 2026: Princesses of the Early Middle Ages
Daughters of kings were often used to seal treaty alliances and forge peace with England’s enemies. Princesses of the Early Middle Ages: Royal Daughters of the Conquest explores the lives of these young women, how they followed the stereotype, and how they sometimes managed to escape it. It will look at the world they lived in, and how their lives and marriages were affected by political necessity and the events of the time. Princesses of the Early Middle Ages will also examine how these girls, who were often political pawns, were able to control their own lives and fates. Whilst they were expected to obey their parents in their marriage choices, several princesses were able to exert their own influence on these choices, with some outright refusing the husbands offered to them.
Their stories are touching, inspiring and, at times, heartbreaking.
Princesses of the Early Middle Ages: Royal Daughters of the Conquest is now available for pre-order.
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell, Elizabeth Chadwick and Scott Mariani, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved.
There are now over 80 episodes to listen to!
Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online bookshop.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly FRHistS