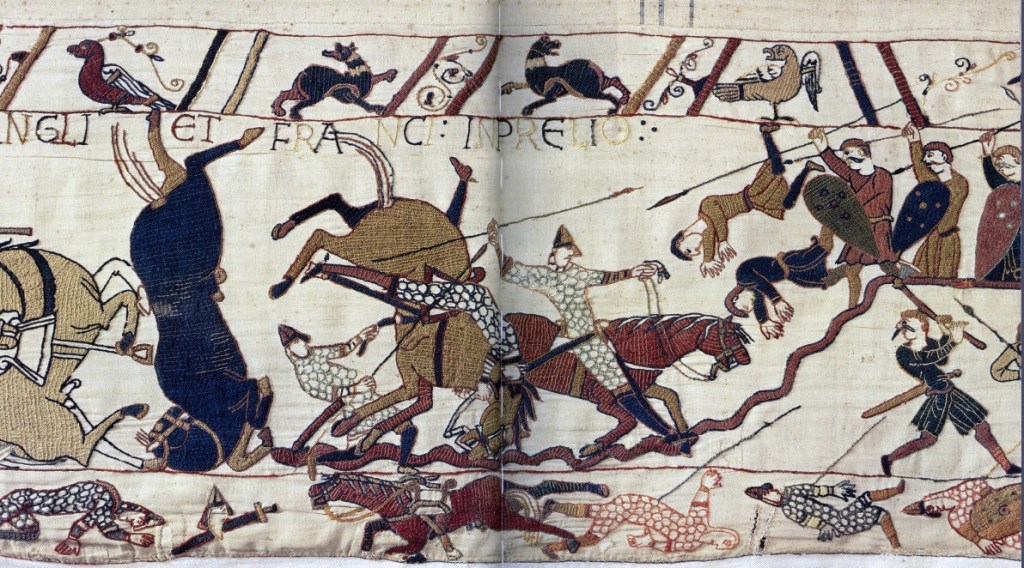
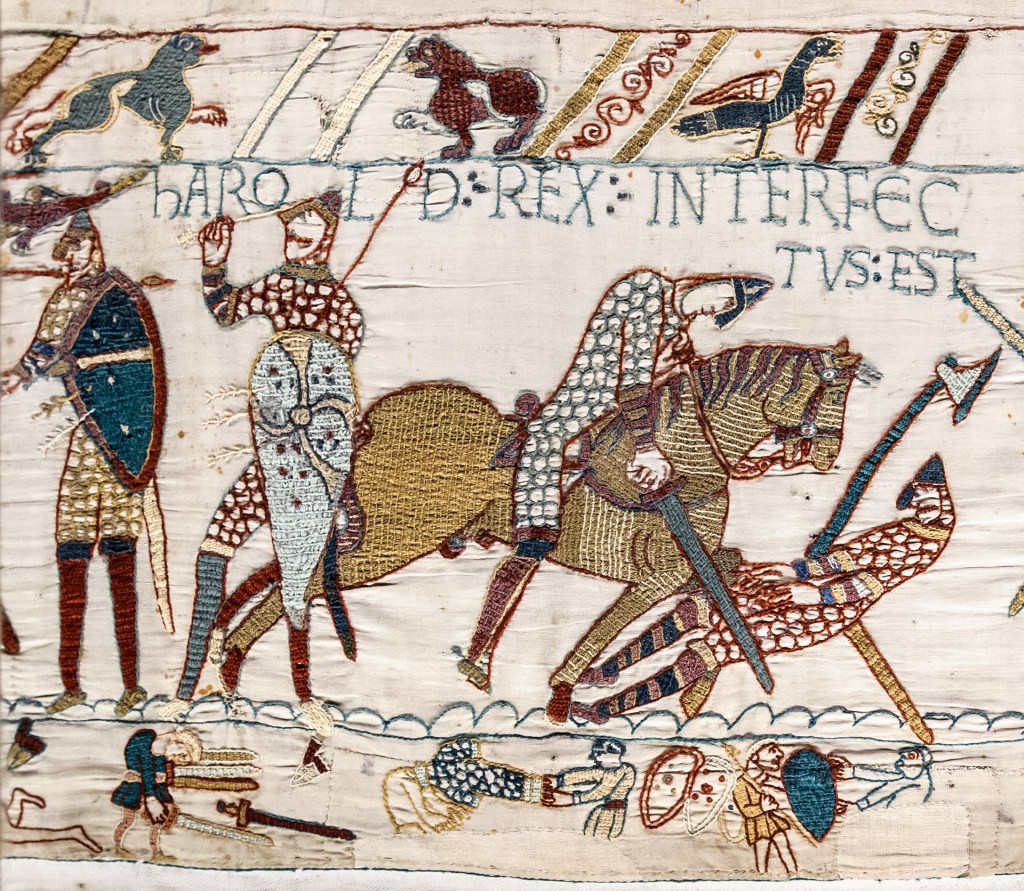
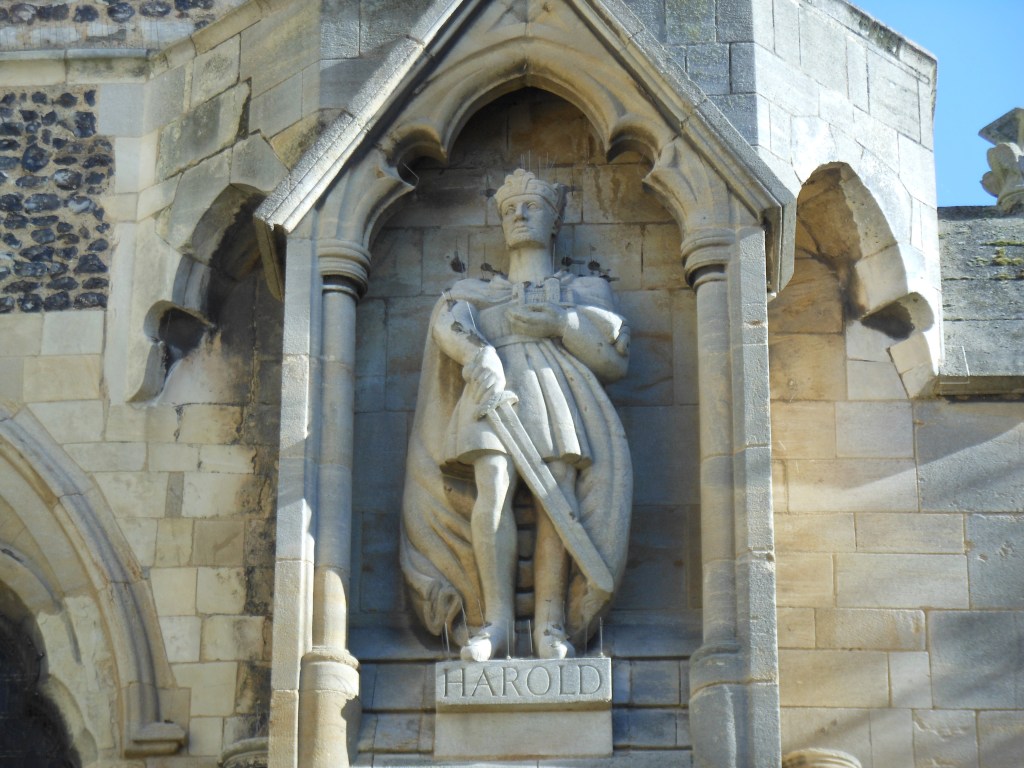
In the third episode of my Wordly Women interviews, I welcome Paula Lofting to History…the Interesting Bits to talk about her writing journey. Paula is the author of the Sons of the Wolf series of novels and has recently published her first none fiction work Searching for the Last Anglo-Saxon King: Harold Godwinson, England’s Golden Warrior.
Welcome Paula….
Sharon: What got you into writing?
Paula: When I was a little girl as soon as I could write straight, I used to come home from school sit at the coffee table in our lounge on my feet and write stories. I was particularly fond of ‘composition’ class at school where the teacher would put several titles up for us to choose from to write about. I often had my stories read out to class.
I guess it was something I always wanted to do. I remember in my teens, writing an epic historical fiction based on the years after the Romans left Britain, but I hand wrote it because I hadn’t learned to type and the typewriter, I had was useless. I thought I was never going to submit because it never occurred to me to just type with one finger! So, I gave up on that idea. I’d written plays, poems, and all sorts of stuff, but I was also in a bad relationship with a man who didn’t want to share me with a pen, so it was difficult until the relationship ended, and I had moved on. It was when the advent of personal computers came along when I realised that I could actually achieve my dream if I wanted to.
Sharon: Tell us about your books.
Paula: I have been writing a series set in the years leading up to the Norman Invasion of 1066. There are currently two books I have published in the series, and of course a nearly finished 3rd WIP. The series is called Sons of the Wolf, which is the name of book 1 and book 2 is The Wolf Banner, and 3 which I am working on is called Wolf’s Bane. As you can see there is a recurring theme. The theme is not something to do with real wolves but has its origins in my hero’s family history whose ancestors believed that they were descended from wolves.
The books tell the story of Wulfhere, a Sussex thegn, and follows the fortunes of his family in the years before the Battle of Hastings took place. It explores the lives of the ordinary people who lived against the backdrop of the political landscape of the time.
The series is a chronological account of events that are woven into the tapestry of the family’s lives and also tells the story of the main historical players of the time, such as Harold Godwinson and his clan. The two men’s lives run parallel alongside each other, and their contrasting stories are intricately woven together as is their fate.
The books all run consecutively, and you will find there are no gaps in the saga, so where one book ends, the new book starts. I have plans to continue after the catastrophic events of 1066 into the rebellion years.
Sharon: What attracts you to the 11th century?
Paula: I think that there is a lot of romance around the whole story of two men who fought over their claims to be king of England which people are drawn to. There is the tragedy of the last ‘Anglo-Saxon king’ who is butchered to death on the battlefield: the tall, handsome, charismatic, affable, warrior who fights for his people and his country. There is the underdog and the overdog theme which comes after the conquest and lasts for some time before England begins to melt as though seamlessly into the new regime.
Then you have the original Robin Hood type story of Hereward who sort of appears from nowhere to fight the good fight against the baddies after coming back to England from abroad to find a lot of things have changed and his ancestral lands commandeered by invaders. There is so much to play with there, a passionate conglomerate of rich history that evokes and inspires in the most amazing manner. It is an era that sets itself apart from what happens later – the cusp of change from the old world to the new.
I find it fascinating. Love… Betrayal… Battles… Bloodfeud.
What’s not to love!
I have also written a book about Harold Godwinson which is due for release any day now with Pen and Sword.
Sharon: Who is your favourite Anglo-Saxon and why?
Paula: There were so many extraordinary characters, and a lot I could choose from. For now, I have to go with Harold Godwinson, simply because, although we will never know what his true nature was for certain, what is written in the sources is constant and conjures up a vision of a man who loved his wife, his family, and his country. A man who avoided internal conflict, forced to navigate intrigue, family skirmishes, and the jealousy of the other aristocracy. He was not a perfect man, but in comparison to many rulers and sub rulers in medieval times, there were a lot more who were far more undesirable. During his early tenure as king, knowing that his country was in danger on many fronts, he acted swiftly to gather his armies together and deploy them to defend the shores. He even found time to see to some of his admin duties, all this in the early weeks of his reign. Who knows what he might have achieved if his life had not been so cruelly taken from him so early into his reign.
Sharon: Who is your least favourite Anglo-Saxon – or Viking – and why?
Paula: Ooo – Can I have one of each?
In that case I have to say, the Anglo-Saxon Ealdorman Eadric Streona whose betrayal of King Edmund lost him the battle of Assandun.
My least favourite Viking would have been Sweyn Forkbeard who was invading England from the 990s up until 1013. He became king for about 6 weeks before he died in February 1014. His pillaging and burning of England really stank.
Sharon: How do you approach researching your topic?
Paula: Well, currently I am taking notes from the two major annals, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicles and the Chronicon ex Chronicis which was the work of the monk, John of Worcester and also in part, someone called Florence. I plan to augment them with other sources that I read, both primary and secondary, to try and find sources that correlate and contradict each other so I can make sure I have all the facts in one place when I come to write the narrative. I am always very grateful to those historians who came before me for having done the hard part of digging through the foundations of the information available to me and try to see the original sources for myself. Its helpful that these authors give guidance in their own work for us new historians to build upon and come up with new ideas.
For Historical fiction I have the privilege of being a reenactor and learning the everyday tasks and the little detailed things that experimental archaeology gives us like clothing, food, buildings and battle strategies that often history texts can’t give us. This helps me to build my world as authentically as I possibly can.
Sharon: Tell us your ‘favourite’ Anglo-Saxon story you have come across in your research?
Paula: Oo I love this question!
I have a few, actually: The research carried by Dan Armstrong regarding the Papal Banner. It seems there is little evidence for it in 1066. Readers will need to read the book to find out more about what Armstrong uncovered.
Another is the version of Harold’s trip to Normandy that the English chronicler, Eadmer of Canterbury writes in his History of Recent Events in England, a story that makes far more sense, even though it is the only version of this you can find. And considering that Eadmer was not particularly pro Harold, I think it is far more reliable than the Norman sources.
I also love the anecdotal tale of Bishop Wulfstan who carried a pair of snips with him to cut the hair long hair of the young men who came before him. He didn’t approve of men with long hair, obviously. Can you imagine, you’re an elite, well-respected member of the elite huscarls kneeling before him as you get to the front to receive holy communion and he reaches over your head and grips your neatly combed and beautifully tied back pony-tail and with one snip, you lose it! And there was nothing you could do about it!
Sharon: Tell us your least ‘favourite’ Anglo-Saxon story you have come across in your research?
Paula: Oh gosh, I can name lots, but probably the worst, I have to say, is the cruel propaganda used by the Norman scribes such as Poitiers, who was the first one to mention the Papal Banner, and the way they defiled Harold’s character to detract from William’s regicide of an anointed king and make him seem like a saint!
Sharon: Are there any other eras you would like to write about?
Paula: Yes indeed, but I’m probably never going to achieve them all, here are just a few:
Staying in the so-called dark ages, I once started to write an epic about the post Roman Britain era, centring on Ambrosius Aurelianus. It never came to anything because my circumstances were not right at the time, but I would love to give it ago one day.
Another is Macbeth, and coming right out of my comfort zone, a story about a highway man.
Sharon: What are you working on now?
Paula: Edmund Ironside is my new project for Pen and Sword – a non-fiction book, and fiction wise, I am working on finishing the third novel in my series, Wolf’s Bane
Sharon: And finally, what is the best thing about being a writer?
Paula: Escaping into other times, other places, and building a different world. It gives me a sense of release and I enjoy creating characters I love.
It has never really been my aim to sell loads of books and earn loads of money from writing because its not going to be achievable in this day and age. Its more of a hobby really, but if people read my work, then I am very happy, especially if they enjoy it. That’s the most important part to me.
About the author:
Paula was born in the ancient Saxon county of Middlesex in 1961. She grew up in Australia hearing stories from her dad of her homeland and its history. As a youngster she read books by Rosemary Sutcliff and Leon Garfield and her love of English history grew. At 16 her family decided to travel back to England and resettle. She was able to visit the places she’d dreamt about as a child, bringing the stories of her childhood to life. It wasn’t until later in life that Paula realised her dream to write and publish her own books. Her debut historical novel Sons of the Wolf, was first published in 2012 and then revised and republished in 2016 along with the sequel, The Wolf Banner, in 2017. The third in the series, Wolf’s Bane, will be ready for publishing later this year.
In this midst of all this, Paula has acquired contracts for nonfiction books with the prestigious Pen & Sword publishers. Searching for the Last Anglo-Saxon King, Harold Godwinson, England’s golden Warrior is due to be published at the end of February, and a biographic of King Edmund Ironside is also in the pipeline. She has also written a short essay about Edmund for Iain Dale’s Kings and Queens, articles for historical magazines. When she is not writing, she is a psychiatric nurse, mother of three grown up kids and grandmother of two and also re-enacts the Anglo-Saxon/Viking period with the awesome Regia Anglorum.
Social Media:
Website: www.threadstothepast.com, Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Wulfsuna?locale=en_GB, Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/paulaloftingwilcox/, x: https://x.com/longshippub, Threads: www.threadstothepast.com, Blue Sky: @paulaloftingauthor.bsky.social
Book Links: Sons of the Wolf; Wolf’s Bane; Searching for the Last Anglo-Saxon King: Harold Godwinson, England’s Golden Warrior.
*
My books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell and Michael Jecks, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved. Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly, FRHistS and Paula Lofting