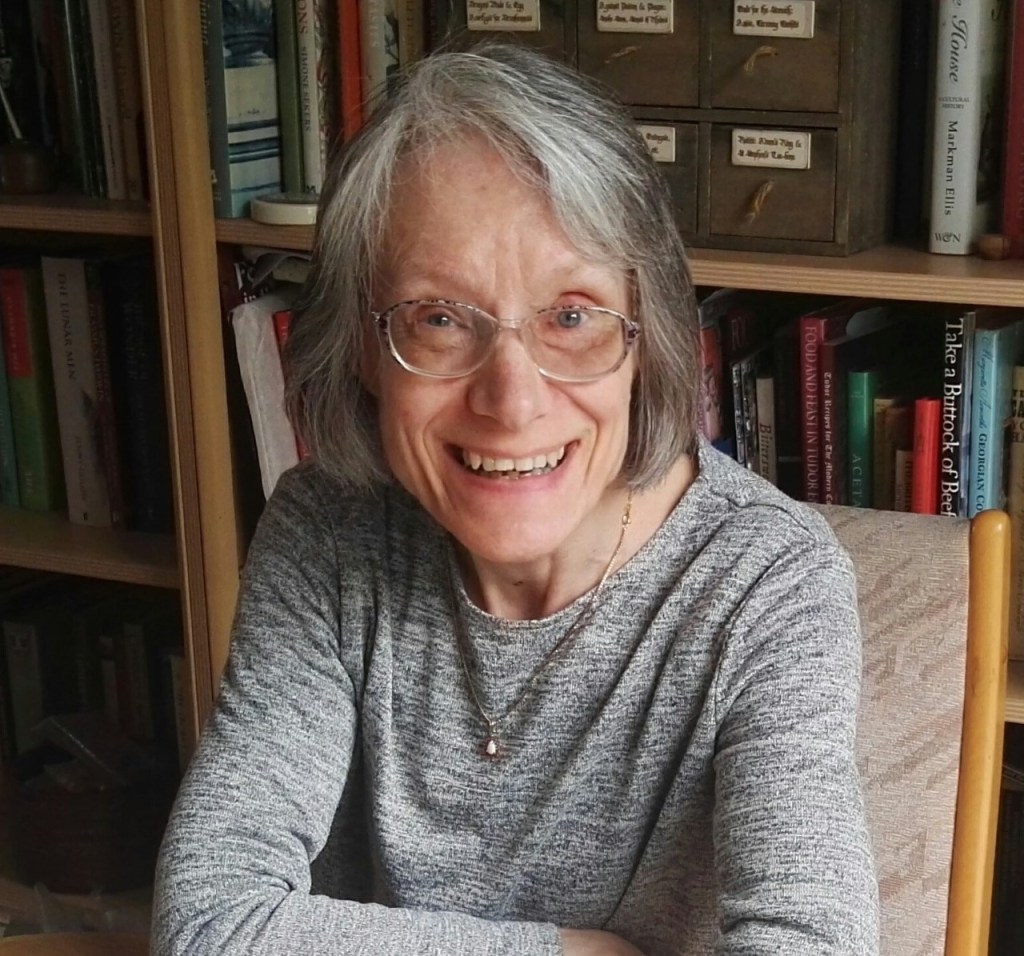
In today’s spotlight on Wordly Women, I welcome my good friend, novelist and historian, Toni Mount back to History… the Interesting Bits. Toni writes the fabulous Seb Foxley mystery novels and the non-fiction series How to Survive in…
Sharon: What got you into writing?
Toni: I’ve always been a story-teller. Aged 6, when the teacher was called away – before the days of teaching assistants – she would have me sit at the front of the class and tell them a story. It was usually a mix of various fairytales with princes, princesses, witches and dragons. I like to think I became more sophisticated when I started writing them down in English Composition lessons aged 7 or 8. My imagined ‘First Flight of Concorde’ – the supersonic plane – won the school prize and my head has been full of stories for as long as I can remember. A good many have made it to the page but not all.
Sharon: You write both fiction and non-fiction – is one harder than the other?
Toni: Fiction needs your own ideas; in non-fiction the facts are there, waiting for you to use. Since my novels are as authentic to the period as I can make them, but without the ‘gadzooks’ and ‘forsooths’, they take as much research as the non- fiction books. In both cases, I’m looking to tell a good story. The difference is that non-fiction may have gaps where historians don’t know the answers, such as what was Edward II thinking when he gave Piers Gaveston the queen’s jewellery but in a novel the writer is allowed to tell you why.
Sharon: Tell us about your books.
Toni: I’ve had 30+ books published, half of them novels. My most successful non-fiction books are ‘Everyday Life in Medieval London’ and ‘Medieval Medicine’ both published by Amberley, and ‘How to Survive in Medieval England’ published by Pen & Sword which was recently a no.1 best seller on Amazon. The How to Survive series – my fourth: ‘How to Survive in Ration-Book Britain’ is due to be out in November 2025 – is written for the armchair time-traveller and puts a light-hearted slant on history. ‘How to Survive in Tudor England’ and ‘How to Survive in Anglo-Saxon England’ are the other titles.
My Sebastian Foxley Medieval Murder Mystery series has quite a following – book 13 ‘The Colour of Darkness’ has just gone off to the publisher MadeGlobal. Seb is a London-based scribe and illuminator in the 1470s-80s whose eye for detail means he spots clues that others miss to solve crimes. Many are true crimes which were recorded in the Mayor’s Court Rolls and remain unsolved – until now. I love the way my characters take over the story, sometimes doing things that never occurred to me. Seb has become a family member, so much so that my sons commissioned a portrait of him for my 65th birthday and it hangs above the fireplace.
Sharon: What attracts you to the period?
Toni: Whether fact or fiction, the Plantagenet period from the 1150s to 1485 is by far the most intriguing for me. Who doesn’t love to puzzle out a mystery? But modern policing is too boring to write about with so much paperwork, hours of CCTV footage to trawl through, fingerprinting, DNA, ballistics, etc. Give me Sherlock Holmes with his magnifying glass every time. The medieval period has even fewer technical complications.
Sharon: Who is your favourite medieval or Tudor personality and why?
Toni: Richard III obviously. I love the controversy. Was he a saint or a sinner? Or simply a human being?
Sharon: Who is your least favourite medieval or Tudor personality and why?
Toni: Henry VIII – a vicious paranoid megalomaniac. What’s to like? (Sharon: I could not agree more!)
Sharon: How do you approach researching your topic?
Toni: I read all I can around the subject; get a feel for the period and ‘live it’ in my head. As I write, if I realise I don’t know something, I make a note of it, check it out and list sources as I go. This is vital for a book which will have references and footnotes but even if I’m working on a novel, I may want to return to a source for further info or to mention it in my Author’s Notes – this is where I tell readers what’s true in the novel, which characters really existed, etc. In ‘The Colour of Darkness’, I did additional research into Medieval Mystery Plays and the ‘Duke of Exeter’s Daughter [a torture device], among other things. For the next novel, I’m reading up on medieval ships and firearms – I think it’s time somebody got shot with a ‘gunne’.
Sharon: Tell us your ‘favourite’ medieval or Tudor story you have come across in your research.
Toni: John/Eleanor Rykenor was a cross-dresser in the 1390s. He claimed to have had sex with nuns ‘as a man’ and didn’t charge them for it but did charge a group of Oxford priests-in-training for his services ‘as a woman’. He/she also said he’d spent a year or more living as a man’s wife. When caught in flagranti in a stable, wearing women’s attire and charging a man for sex, as Eleanor she appeared in court. The authorities weren’t sure what crime to charge her with – homosexuality wasn’t made a criminal offence until Tudor times – so she was charged with misrepresenting the product for sale, i.e. advertising her services as a female without having the appropriate ‘equipment’ for the job. She had to pay a fine for flouting what we would call the Trades Description Act. John/Eleanor is a character in my Foxley novels although he/she lived a century before they’re set. I couldn’t resist using such a fantastic character.
Sharon: Tell us your least ‘favourite’ medieval or Tudor story you have come across in your research.
Toni: The discovery of RIII’s skeleton in a Leicester car park ruined my first ever trilogy [written in 1980s and unpublished]. My premise for the series of novels was that Richard, though wounded, survives the battle of Bosworth and goes on to have further adventures. Henry Tudor, frustrated when he can’t find Richard’s corpse to prove the king is dead, substitutes a crippled beggar to be buried instead. I was about to rewrite the trilogy when the dig discovered the bones and DNA proved it was Richard. How annoying!
Sharon: Are there any other eras you would like to write about?
Toni: Apart from writing about the medieval and Tudor eras, I’ve also written a Victorian who dunnit – ‘The Death Collector’ – making use of unsolved murders from the 1880s, including those attributed to Jack the Ripper. That was great fun to write and I fancy doing a sequel. Also, I wrote a non-fiction book ‘The World of Isaac Newton’ and I think Isaac, with his brilliant brain, has definite possibilities as a sleuth. I’ve published books ranging from Anglo-Saxon England to the 1950s and everything in between has at least been touched upon. Maybe more on the Anglo-Saxons would be interesting.
Sharon: What are you working on now?
Toni: The next novel is brewing: ‘The Colour of Malice’ and two self-published booklets are being prepped. ‘Medieval Christmas’ will do what it says on the tin. ‘Warriors – Men-o’-War’ is a very different beast as a collection of my short stories, something I’ve not done before, from Agincourt to Afghanistan. There are no new titles for non-fiction books at the moment.
Sharon: And finally, what is the best thing about being a writer?
Toni: Playing God with characters [in fiction] and the beauty of words – choosing how best to express your ideas and imaginings on the page. Marvellous!
About the Author:
Toni studies, teaches and writes about medieval history. She is a successful author writing the popular Sebastian Foxley medieval murder series and several non-fiction volumes, including her collection of How to Survive in books. She has created several online courses for http://www.MedievalCourses.com, she teaches history to adults and is an experienced speaker giving talks to groups and societies. Toni enjoys attending history events as a costumed interpreter and is a member of the Research Committee of the Richard III Society.
Toni earned her Masters Degree by Research from the University of Kent in 2009 through study of a medieval medical manuscript held at the Wellcome Library in London. Her first-class honours degree, Diploma in Literature and Creative Writing and her Diploma in European Humanities are from the Open University. Toni also holds a Cert. Ed (in Post-Compulsory Education and Training) from the University of Greenwich.
Find Toni Mount’s books here
Find Toni on Social Media:
Amazon; Website; Seb Foxley website; Facebook: Medieval England Facebook; Seb Foxley Facebook; Twitter
*
My books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell, Elizabeth Chadwick and Michael Jecks, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved. Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly, FRHistS and Toni Mount