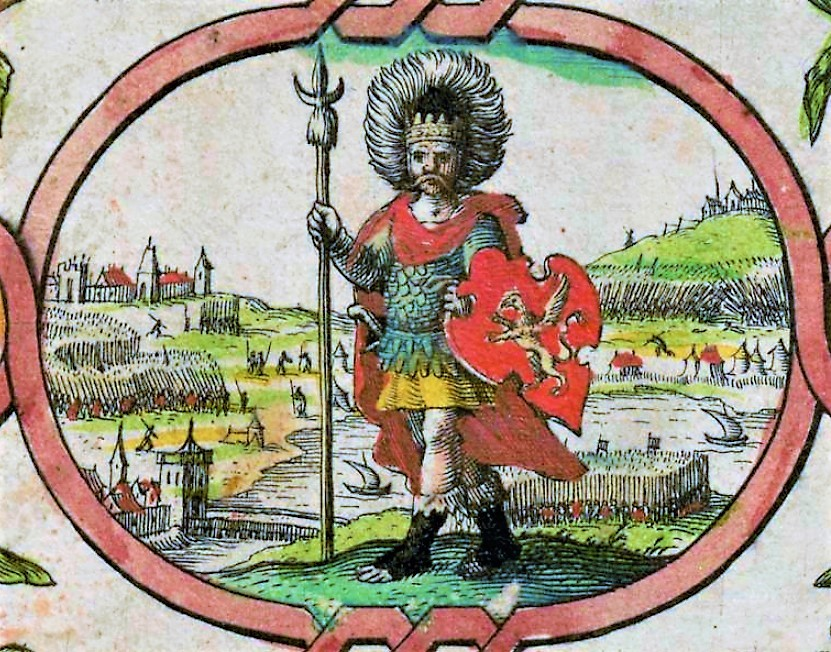
When the Saxons, invited to settle in Britannia by King Wyrtgeorn, brutally murder the father and brother of Ceredig, the second son of a fifth century Romano-British chieftain, he flees the land of his birth.
While the Saxons expand their control over Britannia, Ceredig grows up in Armorica, learning the ways of the Gewisse, and ultimately taking command of this elite force of warriors, who had remained loyal to his father, Elisedd.
Despite ruling as a chieftain in Armorica, Ceredig remains determined to return to his homeland, avenge his father and brother’s murder, and finally reclaim the lands his father had once ruled in southern Britannia.
After over forty years in exile, Ceredig, his son and a force of Gewisse warriors return to Britannia, joining a large army of Britons who are preparing to take on the Saxons in battle at Badonbyrg.
What happens next will go down in history…
As a debut novel, Rise of the First Wessex King by A.J. Proudfoot is a winner. And as a special treat, alongside my review, I have an interview with the author, who is currently working on book no. 2 in what promises to be a fascinating series. Cerdic, or Ceredig, is the founder of the kingdom of Wessex and a royal house that would reach its zenith under Ceredig’s descendants, King Alfred the Great, Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians, her brother Edward the Elder and Edward’s son Athelstan, first king of England.
And it all started with Ceredig.
In Rise of the First Wessex King, A.J. Proudfoot recreates Ceredig’s world, post-Roman Britain, breathing life into this 1,500-year-old story. And what a fascinating story it is. Though our knowledge is limited, Proudfoot fills in the gaps to create a lively and energetic retelling of the foundation of the royal house of Wessex. This is the story of the fight of the native Britons against the invading Saxons, of a war that must have felt never-ending, at times. It is a story of conflict and betrayal, but also of family and comradeship, and of a young man who had to patiently wait for the time to be right to achieve his dream of pushing back the Saxons and going home.
The characters, particularly our hero, are wonderfully vivid. And I love how Proudfoot weaves the legends of Arthur and Hengist and Horsa in to the story, bringing a little-known period of history back to life. Who doesn’t like to see a little bit of King Arthur thrown into the mix? The inclusion of Artorius and Ambrosius made me smile – and want to read more!
This is a debut novel, so Proudfoot sometimes fall into the trap of giving summaries, telling, rather than showing the action and debate, but this does not detract from the pace of the book. Overall, it is a fabulous read, imbued with a sense of adventure. It is a great start to what promises to be an impressive series.
Overall, it is a great story, told well!
If you’re looking for a new author to sink your teeth into, I don’t hesitate to recommend A.J. Proudfoot’s Rise of the First Wessex King.
To Buy the Book:
Books2Read; The Book Guild; Bookshop.org (UK)
Interview with A.J. Proudfoot
Sharon: So, Alex, what got you into writing historical fiction?
Alex: This may come as a surprise, but I didn’t originally set out to become an author and write historical fiction novels. I was simply trying to trace the origins of my unusual Proudfoot surname, and was continuing the research into our Proudfoot family history that my parents and aunt had begun many years before.
After several years’ research, I was amazed to find that I had traced my family ancestry back 1500 years to a mysterious chieftain called Cerdic, at the end of the fifth century, who founded the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex. There are many interesting ancestors in the Proudfoot family tree, whose lives would make an excellent novel, but when I discovered more about Cerdic’s life, I realised that there was an Arthurian story that was worth writing.
Sharon: What made you want to tell Cerdic’s story?
Alex: I was intrigued why this important figure in early English history has been largely ignored by historical writers, so I undertook my own research into the life of Cerdic, finding crucial inconsistencies in what is written about Cerdic’s Saxon heritage, which I put down to a desire, by early Saxon chroniclers, to establish King Alfred’s Saxon ancestry.
Instead, I found evidence that Cerdic was more likely to be descended from a Romano-British family, who originally hailed from an ancient Welsh kingdom, and was more than likely called Ceredig, given his Brythonic heritage, and to the phonetic similarities. As a result, I felt compelled to use what I had learned to tell the story about my earliest known ancestor and his crucial role in history, based on recorded events in the early Anglo-Saxon era. To paraphrase John Wade, the rest is historical fiction!
Sharon: How do you go about researching a historical character from 1500 years ago?
Alex: The great difficulty in researching a historical figure from so far back is the lack of contemporary records. My starting point was, naturally, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, but it only mentions six events relating to Cerdic’s life, and is written from a Saxon perspective. I read all I could about Cerdic in research papers by modern Anglo-Saxon historians, including JNL Myers and Richard Coates, which is where I found clues to Cerdic’s Romano-British connections. There was also a story about 5th century Bishop Germanus meeting a regional chieftain in southern Britain, called Elasius, whose name is remarkably similar to Elesa, the recorded name of Cerdic’s father in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle.
Eventually, I had built a picture of the young son of a Romano-British chieftain, ruling and defending the southern coastline of Britain against Saxon invaders, who suddenly disappeared from Britain, returning nearly fifty years later to take control over a region in the Upper Thames Valley, before expanding his lands south before becoming king and ruling a kingdom of the Gewisse that would eventually become known as Wessex, named after the West Saxons.
My research raised more questions than answers, so I used what I had learned about events during that period to write a dramatic reconstruction of Cerdic’s life, and the formation of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex. Based on fact, but mostly fiction.
Sharon: What are you working on now?
Alex:I am currently working on a sequel to Rise of the First Wessex King, which will follow the lives of Cunorix and his son, Ceawlin, as they try to build on Ceredig’s legacy in ruling the kingdom of the Gewisse, whilst facing threats from the Saxons in the east, and Britons in the west, as well as challenges they could not anticipate.
Sharon: What is the best – and worse – thing about being a writer?
Alex: Personally, the hardest part about writing my historical fiction novels is that the stories are based in the south of England and I live just outside Edinburgh, in Scotland. This meant that I have had to make several research trips down south, visiting locations featured in my novels. Whilst there is very little evidence to reveal what it would be like when the books are set, I have found this a useful exercise in understanding the topography, as well as encouraging the creative writing juices.
The best part of being a writer is that I love history and solving puzzles. This has been useful in writing about a period in history where facts are limited, so deciphering my characters’ motives behind their decisions has been crucial in building the story of their lives.
About the Author
A J (Alex) Proudfoot lives in Musselburgh, near Edinburgh. He started his career as an accountant, working in the brewing, publishing and financial sectors, before qualifying as a chartered marketer, working at the University of Edinburgh for over twenty years. After retiring early in 2018, he has spent his free time researching his Proudfoot family history, back 1500 years to his earliest known ancestor, which led to the publication of his debut historical fiction novel, Rise of the First Wessex King.
Social media links
Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/ajproudfootwriter
YouTube – https://www.youtube.com/@ajproudfoot
Book trailer – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4gpZMOMzwZs&t
*
My books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
‘Scotland’s Medieval Queens gives a thorough grounding in the history of the women who ruled Scotland at the side of its kings, often in the shadows, but just as interesting in their lives beyond the spotlight. It’s not a subject that has been widely covered, and Sharon is a pioneer in bringing that information into accessible history.’ Elizabeth Chadwick (New York Times bestselling author)
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell and Michael Jecks, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved.
Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly, FRHistS