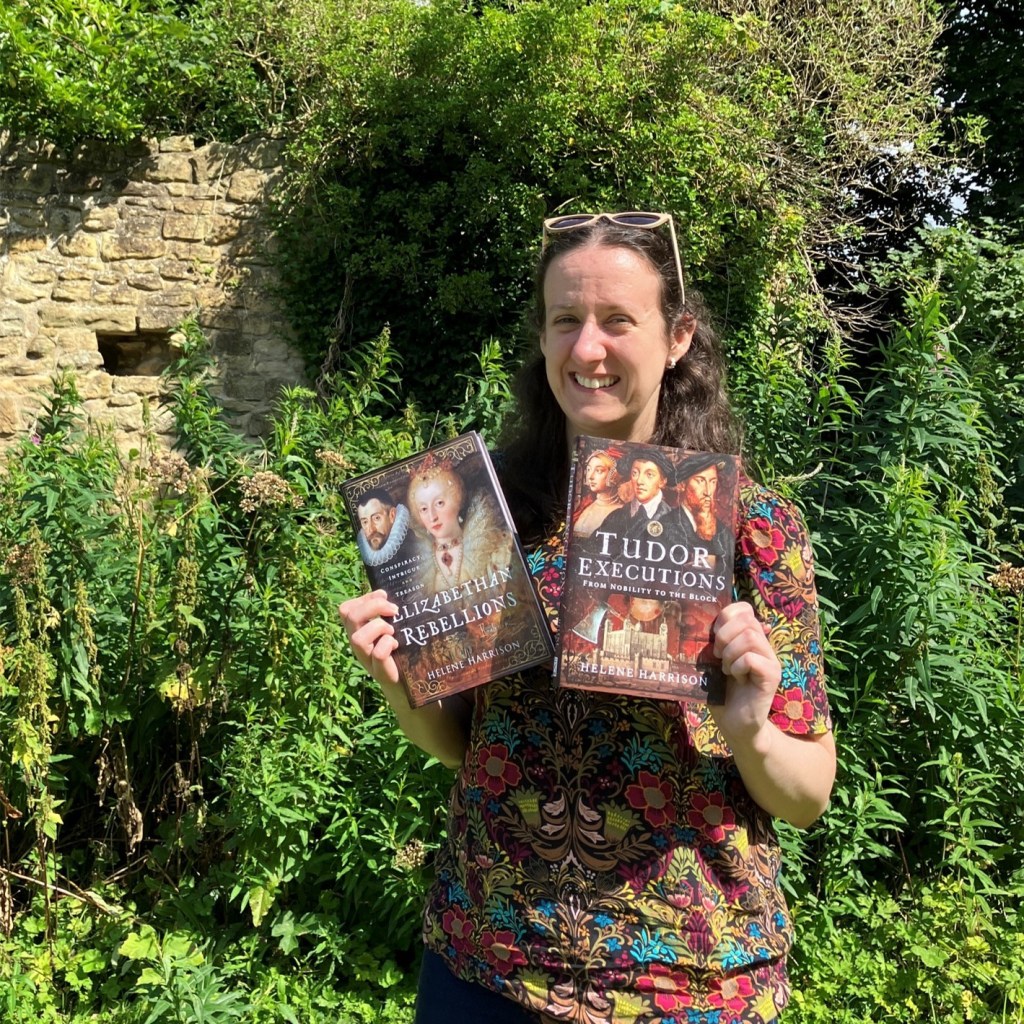
I have been inspired by the British Library’s Medieval women: In Their Own Words exhibition to launch a series of interviews featuring women writers of History, Wordly Women, to give us an insight into their books, their writing habits and themselves. My guinea pig – er, I mean – first Author Spotlight is the wonderful Helene Harrison, author of two fabulous books on the Tudors, with a third on the way.
So, over to my chat with Helene…
Sharon: What got you into writing non-fiction?
Helene: ’ve always enjoyed research, no matter on what topic. But it was during my A Levels that I really got into history, which then developed at university during my undergraduate and postgraduate degrees. When I finished my undergraduate degree in 2012, I started my blog, Tudor Blogger, because I felt a bit bereft, even though I was about to start my postgraduate degree. It took off from there really, as I started reviewing history books in my collection on my blog and then publishers started to send me books to review. I was then approached by my publisher to ask if I was interested in writing a book for them and that’s how writing non-fiction came about really. I’d always wanted to, but I didn’t think anyone would actually be interested in reading them.
Sharon: Tell us about your books.
Helene: My first book was ‘Elizabethan Rebellions: Conspiracy, Intrigue and Treason’ which was published in January 2023. It still didn’t really feel real that I was a published author even when I held it in my hands! My second book ‘Tudor Executions: From Nobility to the Block’ was then published in July 2024. I’d been researching Tudor executions and treason as an interest for several years anyway, so I had a lot of the background in my head already. My third book ‘The Many Faces of Anne Boleyn: Interpreting Image and Perception’ is due to be released in July 2025 and is now available for preorder. This upcoming one is the one I’m, I think, most nervous about. It has developed from my undergraduate and postgraduate history degrees which looked at Anne Boleyn’s public image (undergraduate) and then at perceptions in literature and film (postgraduate). This book combines the two and builds more on it. I didn’t feel quite ready to write this book when I wrote my first two, but this felt like the right time.
Sharon: What attracts you to the Tudors?
Helene: When I was doing my A Levels, I did a module on Tudor Rebellions, which is really where I delved into Tudor research, though I had some very basic knowledge before that. My GCSE had been in modern world history, so I didn’t really have an earlier chance to do proper research on the Tudors. At university I did modules on early modern women’s history which included witchcraft and women in power which ignited my passion for Anne Boleyn and Elizabeth I. Showtime’s TV show, The Tudors finished its final series while I was at university, and that just added to my interest, wanting to know what was real and what was fiction, and that really fuelled the subjects of my dissertations. But I think that what really attracts me to the Tudors today is that they seem to be quite a unique dynasty, but that their blood still feeds down into the royal family today. The Tudors won the throne in battle, and that was the last time an English monarch died in battle, and we also see the advent of successful female monarchy. England rises as a global power, and we begin to see the reach extending beyond the British Isles in an age of exploration, great literature, and new ways of exercising power.
Sharon: Who is your favourite Tudor and why?
Helene: This will probably be the same answer as a lot of people, but Anne Boleyn. She is such a fascinating figure, more than the first beheaded wife of Henry VIII. Her upbringing was singular for a woman of her class, being raised at the courts of the Low Countries and France, exposed to new religious ideas and with an exoticism which marked her out at the English court. Anne was at the centre of massive changes happening in England, in many ways the catalyst for them, and that’s why she has held my interest for so many years. But I do also have a soft spot for Anne of Cleves, and I’m fascinated by Mary Boleyn and her daughter, Catherine Carey Knollys, as well.
Sharon: Who is your least favourite Tudor and why?
Helene: I often think it’s difficult to have a least favourite Tudor because they’re all fascinating in their own ways, even those that perhaps aren’t very likeable. I find Henry, Lord Darnley, the second husband of Mary Queen of Scots, quite difficult to like, but then the suspicious circumstances surrounding his death are so interesting! I also find it very difficult to find redeeming qualities in Thomas Howard, 3rd Duke of Norfolk, who saw two nieces, a nephew, and a niece-in-law, as well as his own son, executed, but always managed to save himself. In the sources he comes across as very cold and self-serving, willing to do whatever it took to save himself, even if it meant his own family being executed. But he was active over a large period of the first half of the long Tudor century, so he is important to study.
Sharon: How do you approach researching your topic?
Helene: Often it depends on the topic! With my second book ‘Tudor Executions’ I had a lot of the secondary source knowledge already, and quite a bit of the primary source knowledge. With my first book ‘Elizabethan Rebellions’ there was a lot more that I didn’t know, so I wanted to make sure that I covered as much as I could from both primary and secondary sources. But I always think it’s important to make sure that you go back to the original sources as much as possible and form your own opinions. Others might disagree with what you think, but I think that it’s important you know your own thoughts before reading those of others otherwise you might be unduly influenced by them. With my third book ‘The Many Faces of Anne Boleyn’, this was a very different approach to research because I knew the primary and secondary sources really well anyway from nearly 15 years of reading and research, but this book does a close analysis of a selection of sources including television, film, novels, and theatre, so there was a lot of analysis of those with comparisons to primary and secondary sources. I started by going back to my undergraduate and postgraduate dissertations, then branching out from there to know what I thought at the time and how my opinions have changed, which they have in some ways! So that was a really interesting way of approaching it, and very different to things I’ve done before!
Sharon: Tell us your ‘favourite’ Tudor execution story.
Helene: Hmm, tricky! Anne Boleyn is always an interesting one, but I know it so well that I thought it would be a relatively easy chapter to write, but I went so far over my word count on that chapter that I really had to work to trim it back! I was very aware that I wanted each chapter to be the same length so that one person wasn’t getting more attention than any other. I did achieve that! I find the Earl of Warwick’s story interesting, but also so sad to write about. Nathen Amin’s work on the Tudor Pretenders was invaluable in working on that chapter. It’s the first execution I discuss in the book and the only one under Henry VII so I was very aware of that, and of how unjust it was, so that may have been my favourite chapter to write actually. The Earl of Warwick was imprisoned in the Tower for fourteen years before his execution, and he was only 24 when he died. It just seems like such a wasted life.
Sharon: Tell us your ‘favourite’ Elizabethan rebellion story.
Helene: My favourite of the rebellions to write about was undoubtedly the Babington Plot of 1586. There was so much intrigue with that one. The Ridolfi and Throckmorton Plots never really quite got off the ground, and neither did Babington, but we have the added knowledge that it was the Babington Plot that led directly to the execution of Mary Queen of Scots, which was really a pivotal moment in Elizabeth’s reign, and in the history of monarchy in the British Isles as well. The Babington Plot had letters being smuggled in beer barrels, ciphers and codes, international conspiracy and plots to invade, and it all being known about seemingly from the beginning by the English government. How far was it all manipulated by Francis Walsingham? The early spy networks of Walsingham his codebreaker Thomas Phelippes I could have written so much more about!
Sharon: Are there any other eras you would like to write about?
Helene: I am fascinated by the royal women of the Wars of the Roses – Margaret of Anjou, Jacquetta of Luxembourg, Elizabeth Woodville, Margaret Beaufort, and Isobel and Anne Neville. I would like to write more about them in the future, perhaps just on my blog though, as there do seem to be more books about them coming out now, both fiction and non-fiction. But if I hadn’t done by undergraduate dissertation on Anne Boleyn and started all of this, my second choice was to do something on the Holocaust. Very different, I know! My grandma was Austro-Polish and was in a labour camp during the Second World War before she moved to England, so that personal connection, in a way, to it I think has just made me more interested. It’s the psychology that I struggle to understand more than anything. I also have an interest in the Jack the Ripper case, though there is so much written on that, I don’t think my kind of amateurish interest will merit much in the way of writing.
Sharon: What are you working on now?
Helene: I am currently waiting for my final set of edits for my third book ‘The Many Faces of Anne Boleyn: Interpreting Image and Perception’ which I then need to index, which is always time-consuming to do right. I am also currently writing my fourth book, also for Pen and Sword, which is about Henry VIII’s Great Matter and his quest for an heir, which has been really interesting to delve into; I wanted to look at it from a people perspective rather than the parliamentary and legal standpoint, how it affected the people involved at different stages and how Henry VIII changed throughout. I’m just over halfway writing that one now, and I am commissioned for a fifth book after that, though I’m keeping mum on the topic of that one for the time being, though it is still firmly in the Tudor period!
Sharon: And finally, what is the best thing about being a writer?
Helene: That one’s easy actually! The best thing I’ve found about being a writer is the history community. Blogging is one thing, but when you’re writing and publishing, you become part of this community, and everyone is so lovely and helpful, and I’ve made some wonderful friends and met some lovely people through it. Amy McElroy and I released our first books on the same day back in January 2023 and have since twice met up in person in London, going to exhibitions at the National Portrait Gallery and British Library. It is definitely the engagement with like-minded people that is so great, and though I was incredibly nervous doing podcast interviews at the start, now I’m a lot more relaxed and I think that’s because the people you’re talking to are just as passionate about history as you are, and they are just so great at putting you at ease and they want you to succeed.
Huge thanks to Helene for such a fascinating discussion. Do take a look at her books – the links are below.
About the Author:
Helene Harrison studied at the University of Northumbria in Newcastle, achieving both a BA and MA in History before going on to complete an MSc in Library Management. Her passion for Tudor history started when studying for A Levels and completing a module on Tudor rebellions. Her master’s dissertation focused on portrayals of Anne Boleyn through the centuries, from contemporary letters to modern TV and film adaptations. Now she writes two blogs, one Tudor history and one book-related, and works in the university library of her alma mater. In her spare time, she loves visiting royal palaces and snuggling up with a book or embroidery project. Her previous books are ‘Elizabethan Rebellions: Conspiracy, Intrigue and Treason’ and ‘Tudor Executions: From Nobility to the Block’, both published by Pen and Sword. Her third book, ‘The Many Faces of Anne Boleyn: Interpreting Image and Perception’, is due out in July 2025.
Where to find Helene:
Website – Substack – Facebook – Instagram – Blue Sky – Threads
To buy Helene’s books:
Elizabethan Rebellions: Conspiracy, Intrigue and Treason is available from Pen & Sword Books (though you can contact me directly on social media or through my website if you would like a signed copy of Rebellions). Tudor Executions: From Nobility to the Block is also available from Pen & Sword Books. The Many Faces of Anne Boleyn: Interpreting Image and Perception is currently only available for preorder through Amazon and Waterstones
*
My books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell and Michael Jecks, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved. Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly, FRHistS and Helene Harrison