I don’t usually start my articles with a disclaimer, but with this one, I think I will. The Princes in the Tower is always a hot topic, after all. So, I will warn you. Here, I am going to look into the life of Lady Katherine Gordon, rather than the veracity of the claim of her husband, Perkin Warbeck/Prince Richard, to being the younger of the two lost Princes. I am giving you the information and evidence that Katherine would have been presented with at the time, and not making any actual judgements. I will leave that to others who have spent much more time on the study of the Princes than I.
Lady Katherine Gordon was, by all accounts, a beautiful woman, with connections, though distant, to the Scottish royal family. She was the daughter of George Gordon, second Earl of Huntly, and his third wife, Elizabeth Hay. George Gordon had previously been married to Annabella Stewart, a great-aunt of James IV, meaning that Katherine was distantly related to the king by marriage.
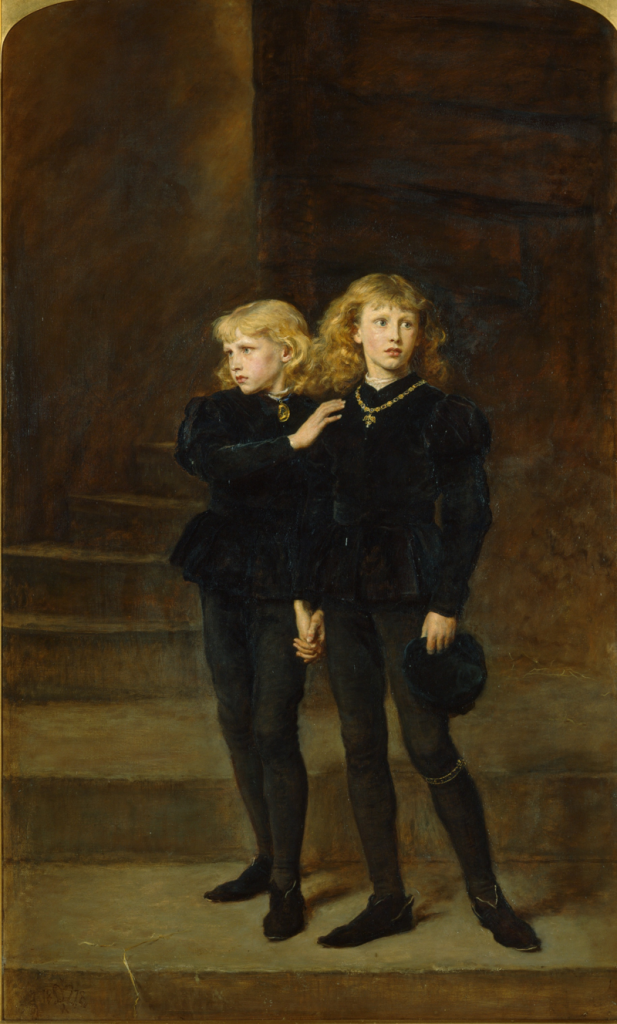
Katherine first came to prominence in 1496, when she was given as a bride to Richard, Duke of York, the younger son of Edward IV and one of the Princes in the Tower. ‘Richard’ had recently emerged from hiding to claim the English throne, and after having spent some years on the Continent had been welcomed at the Scottish court in the autumn of 1495, probably simply to antagonise the English king, Henry VII, rather than in a genuine belief in his claim to be one of the lost princes. It would later be revealed that Richard was actually an impostor named Perkin Warbeck, from the Flemish city of Tournai. But that was by no means clear when he was residing at the Scottish court and several Continental royals, including the lost prince’s aunt Margaret of York, Duchess of Burgundy, had supported his claim to be Richard, Duke of York.
King James IV was probably hedging his bets as to Richard’s real identity when he offered Katherine Gordon in marriage. Katherine had just enough royal credentials to be a suitable bride for an English prince but was not too royal that King James would be embarrassed should Richard prove to be an impostor. And if Richard was successful in overthrowing Henry VII and claiming the English throne, James would have a friend as his neighbour in England. For James, it was worth the gamble and for Richard, it meant that he could count on Scottish support. The Scots king welcomed Richard to court with all honours due to an English prince. He treated Richard like an honoured royal guest, dressed him like a king, gave him a pension and took him on a progress through the kingdom. There is a letter purportedly written by Prince Richard to Lady Katherine in December 1495, just weeks before their wedding, which suggests he is highly enthusiastic about the match:
Most noble lady, it is not without reason that all turn their eyes to you; that all admire, love, and obey you. For they see your two-fold virtues by which you are so much distinguished above all other morals. Whilst, on the one hand, they admire your riches and immutable prosperity, which secure to you the nobility of your lineage and the loftiness of your rank, they are, on the other hand, struck by your rather divine than human beauty, and believe that you are not born in our days, but descended from Heaven.
All look at your face, so bright and serene that it gives splendour to the cloudy sky; all look at your eyes as brilliant as stars, which makes all pain to be forgotten, and turn despair into delight; all look at your neck, which outshines pearls; all look at your fine forehead, your purple light of youth, your fair hair; in one word, at the splendid perfection of your person; and looking at, they cannot choose but admire you; admiring, they cannot choose but love you; loving, they cannot choose but obey you.
I shall, perhaps, be the happiest of all your admirers, and the happiest man on earth, since I have reason to hope you will think me worthy of your love. If I represent to my mind all your perfections, I am not only compelled to love, to adore, and to worship you, but love makes me your slave. Whether waking or sleeping, I cannot find rest or happiness except in your affection. All my hopes rest in you, and in you alone.
Most noble lady, my soul, look mercifully down upon me your slave, who has ever been devoted to you from the first hour he saw you. Love is not an earthly thing, it is heaven born. Do not think it below yourself to obey love’s dictates. Not only kings, but also gods and goddesses have bent their necks beneath its yoke.
I beseech you, most noble lady, to accept for ever one who in all things will cheerfully do your will as long as his days shall last. Farewell, my soul and my consolation. You, the brightest ornament of Scotland, farewell, farewell.1
The marriage between the man claiming to be Richard of York and Katherine Gordon was celebrated on 13 January 1496. Richard was given a white damask ‘spousing’ gown for the occasion. Other gifts included a purple damask-covered suit of armour, six servants, two trumpeters and a French armourer. Richard was also awarded an annual pension of £1, 344.2 The ceremony was followed by a series of jousts in which the king of Scots himself participated, though there is no evidence that Prince Richard did; he probably watched the jousts in the company of his bride. Katherine was now referred to as duchess of York. The newlyweds then travelled with the king to the palace at Falkland in Fife to wait out the winter in anticipation of the campaigning season and Richard’s invasion of England to claim the throne.
James, too, was intent on invading England, despite pressure from both the Spanish and French monarchs. James insisted that the English had started the conflict by destroying his ships and cattle. In September 1496, James invaded Northumberland but returned to Scotland after only three days – no one in England had risen in support of Richard, Duke of York. As the year 1496 ended, Richard was no closer to invading England and was spending less time with King James, instead staying with his wife Katherine at Falkland Palace. In the meantime, King Henry VII’s spies had been at work on the Continent, discovering the true identity of Prince Richard.
King James IV’s priorities now changed. He was seeking peace with Henry VII, and a bride. In July 1497, James was negotiating with Henry to marry the English king’s eldest daughter, Margaret, though she was only eight years old at the time. Henry VII made one of the conditions of the peace that James ‘delyvere unto us Perkyn Werbek’.3 Although the Scots king was amenable to the suggestion, Warbeck was not available to be handed over to the English.
On 6 July, he and his wife set sail from Ayr after 19 months in Scotland. He left behind a brown horse, to be used to settle any debts that may still be outstanding. The ship, a French merchant vessel known as the Cukow, carried Warbeck, Katherine and 30 of Warbeck’s followers. Its hold was stocked with provisions including wine, bread, salt beef, mutton, cheese and fish. Although the king had not been present to bid them farewell, he had provided Katherine with some cloth to make a gown suitable for wearing aboard ship. What had spurred Warbeck to leave Scotland at this particular time is unclear. It may have been the burgeoning peace between James IV and Henry VII, or it may have been news of the Cornish uprising, which had erupted after King Henry had implemented a tax to raise funds for war against Scotland. It may be that Warbeck thought to join this rebellion.
Katherine and her pretender-prince sailed first for Ireland, arriving in Cork on 25 July 1497. After spending a month in Ireland trying to raise troops to their cause, they sailed for Cornwall, making landfall at Whitesand Bay on 7 September with a small flotilla with just a hundred or so people on board. Warbeck’s first action after landing was to make his way to the parish of St Buryan, four miles inland, where he left Katherine to await news of his military campaign. He then headed further into Cornwall, recruiting along the way. It is estimated that by the time he reached Bodmin, Warbeck had an army of between three and five thousand men. After failing to take Exeter from the earl of Devon, Warbeck and his forces marched towards Taunton. The earl of Devon then set off in pursuit and cut off his line of retreat back into Cornwall.
Another royal army moved down from Oxfordshire into Somerset, reaching Glastonbury on 19 September, the same day Warbeck had reached Taunton – just twenty miles away. Warbeck was cornered and, losing his nerve, attempted to flee in the dead of night. With only sixty men, Warbeck sought sanctuary at Beaulieu Abbey in Hampshire on 22 September. Where most religious houses that offered sanctuary could only provide it for a limited period of forty days, Beaulieu was one of those with an exemption, which meant those seeking it could remain in sanctuary there for the remainder of their lives. By early October, Warbeck had been persuaded to surrender and under strong guard was taken to face the king, who was now at Taunton.

The king and his prisoner then proceeded to Exeter where Perkin Warbeck was reunited with his wife. Katherine had been retrieved from St Buryan’s by a force sent by King Henry. When she was found, she was dressed in robes of mourning, which may suggest that she had already been apprised of her husband’s failure, or that she had recently lost a child. We do not know. As the young woman was presented to Henry VII, she was ‘ashamed and tearful’.4 The chronicler Polydore Vergil described the meeting: ‘When the king saw the woman’s beauty he promptly judged her worthy to be among the captive hostages of a general rather than a common soldier.’5 The king perceived Katherine’s nobility and resolved to afford her a more honourable status than he had previously planned. This meant, inevitably, that she would be separated from Warbeck.
Warbeck had been promised his life, but in the same interview the king insisted that Perkin Warbeck publicly admit, in front of his wife, the extent of his deception; that he was not, in fact, the duke of York, and that he was an impostor from Tournai. It may well be that Katherine was not wholly surprised by the confession. She must have heard the stories and accusations, but to hear the confession from her husband’s lips must have been hard to take. She was not duchess of York, she was Mrs Perkin Warbeck. The revelation put their very marriage in doubt. He had married her under a false identity, as Richard, Duke of York. Katherine put herself into the hands of the king.
Henry VII treated Katherine kindly, though he would not send her back home to Scotland. Instead, she was sent to London to serve in the household of Queen Elizabeth. The king purchased horses and saddles for her journey and presented Katherine with new clothes, including a satin gown and a black velvet bonnet. Katherine arrived at Sheen on 21 October and was presented to the queen, the woman she had believed to be her sister-in-law until Warbeck had made his confession. Katherine was given a position in the queen’s household and a pension, not as the wife of the pretender, but in her own right as a high-ranking Scottish noblewoman. When the king returned to London, bringing Warbeck with him, the two lived separately within the royal household. They were well treated but not permitted to sleep together. Katherine also resumed her maiden name.
In June 1498, in spite of the lenient treatment he had received from the king, Perkin Warbeck chose to abscond from Westminster Palace. He was recaptured within a couple of days, having only reached the Carthusian priory at Sheen, just seven miles from Westminster. Although he still escaped the executioner’s axe, the king was no longer minded to be so lenient and sent Warbeck, after a spell in the stocks, to close confinement within the Tower of London.
Katherine’s own situation does not appear to have been threatened by Warbeck’s recklessness and in June 1499 she accompanied the king and queen to Calais for a meeting with Archduke Philip and his wife Juana of Castile, the sister of their future daughter-in-law Catherine of Aragon. Later in the same year Perkin Warbeck, having tried to escape with fellow prisoner Edward, Earl of Warwick, was accused of conspiring against the king. And this time he was not going to get away with it. As it had been established that he was not noble, Warbeck was executed by hanging, not beheading, at Tyburn on 23 November 1499. Warwick was beheaded on Tower Hill five days later.
Katherine’s marital status had been ambiguous since the discovery of Warbeck’s deception, but she was now definitively free to remarry. We know not whether she was saddened or relieved at the execution of Warbeck. She may have felt nostalgic for the short time they had been together, or grateful that the man who betrayed her was no longer able to cast a shadow over her life and future; or both. We will never know. Katherine remained at court and as one of the queen’s ladies was present at the betrothal ceremony of James IV and Margaret Tudor, held at Richmond in January 1502. When the queen, Elizabeth of York, died in February 1503 Katherine was one of the chief mourners at her funeral, accompanying the procession from the Tower of London to Westminster Abbey behind the queen’s sisters. And at the Abbey, she laid her pall on the coffin, again, after the queen’s sisters. After the queen’s death, Katherine remained at court, keeping the king company: she played cards with him, acquired medicines for him when he was ill and painted cloths and religious scenes to be held before him as he lay dying.
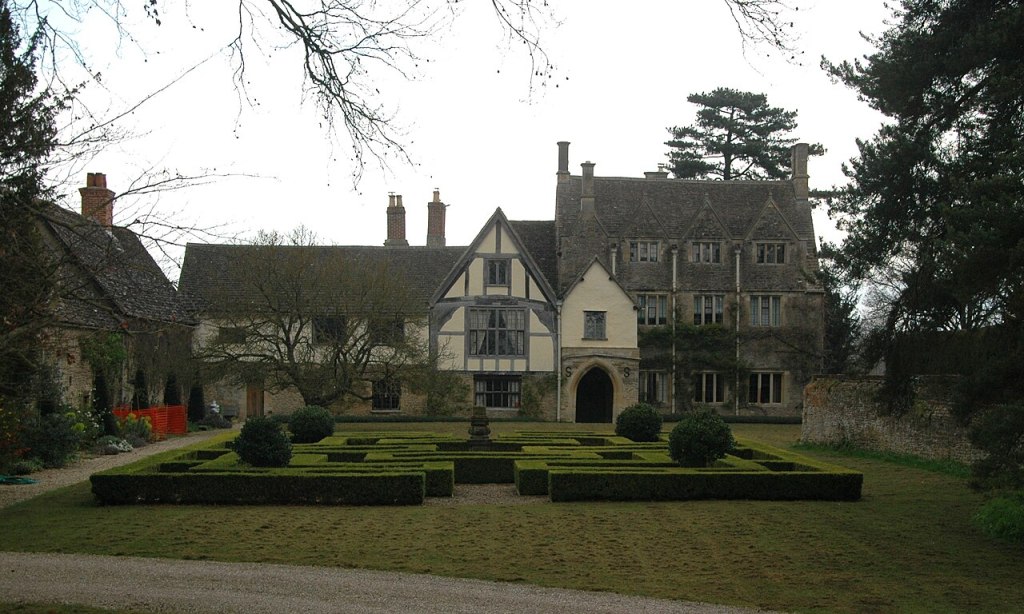
After Warbeck’s fall, Katherine Gordon had been taken prisoner, but her noble status had allowed her to be accepted at court as one of the queen’s ladies. Katherine never remarried in the lifetime of either Elizabeth of York or Henry VII. She was no longer a prisoner, but still not entirely free. Shortly before Henry VII’s death, Katherine was granted land in Berkshire, on the condition that she would not leave England. Following Henry VII’s death, sometime between 1510 and 1512 Katherine married James Strangeways, a Gentleman Usher of the King’s Chamber, but he died in 1516, leaving all his property to Katherine. The following year, Katherine married Matthew Craddock, a Welsh knight from Glamorganshire, obtaining permission to live with him in Wales; her promise to never leave England making such a request necessary. From 1525 to 1530, Katherine was employed in the household of Henry VIII’s daughter Mary as Chief Lady of the Privy Chamber. Katherine was widowed once again in 1531, with Craddock making her executor of his will and leaving her income from some of his Welsh properties in addition to 500 marks. Sometime before 1536 Katherine married for a fourth and final time. Her husband, Christopher Ashton, was a Gentleman Usher of the Privy Chamber. Katherine spent the last years of her life on her lands in Berkshire, at Fyfield Manor.
Survived by her last husband, she died on 14 October 1537, forty years almost to the day after Perkin Warbeck had been captured at Beaulieu Abbey. In her will she refers to all of her husbands, save Warbeck. She leaves bequests to Margaret Kyme, the daughter of Elizabeth of York’s sister, Cecily, to her servant, Philippa Hulls and to Alice Smyth, whom Katherine refers to as her sister.6 Perhaps she was a sister of one of Katherine’s husbands. There is no mention of any children and although there has been speculation that Katherine and Warbeck had a child, there is no evidence of this beyond a report by the Venetian ambassador Adrian Trevisano from September 1497,in which he says Warbeck had arrived in Cornwall ‘leaving behind his wife and children’.7 This may well have been a misunderstanding as there is no further mention of children from Trevisano or any other sources. Katherine was buried in the chancel of the church of St Nicholas at Fyfield. A tomb there, missing its brasses, is still referred to as Lady Gordon’s Monument.
Lady Katherine Gordon had survived the fallout from her first husband’s rebellions and conspiracies and made a life for herself at the English court. She appears to have been considered a dupe to Warbeck’s plotting, rather than a co-conspirator. Her position as the daughter of a Scottish earl and a distant relative of the king of Scots afforded her the chance to make a new life for herself as one of the queen of England’s ladies and she grabbed the opportunity in both hands. She went from being a royal captive to a trusted and loved member of the English court. Not all female prisoners would be so fortunate.
Notes:
1. ‘December 1494’ in CSPM pp. 72-79 quoted in Nathen Amin, Henry VII and the Tudor Pretenders, p. 219; Nathen Amin, Henry VII and the Tudor Pretenders, p. 220; 3. ibid; 4. Bernard André quoted in ibid, p. 269; Polydore Vergil quoted in ibid, p. 269; 6. Susan Abernethy, ‘The Life of Lady Katherine Gordon’; 7. Nathen Amin, Henry VII and the Tudor Pretenders, p. 327
Images:
Courtesy of Wikipedia except the Tower of London which is © 2024 Sharon Bennett Connolly FRHistS
Further Reading:
Nathen Amin, Henry VII and the Tudor Pretenders; Susan Abernethy, ‘The Life of Lady Katherine Gordon’; Amy Licence, The Sixteenth Century in 100 Women; Amy Licence, In Bed with the Tudors; Erin Lawless, Forgotten Royal Women: The King and I; David Loades, editor, Chronicles of the Tudor Kings: The Tudor Dynasty from 1485 to 1553: Henry VII, Henry VIII and Edward VI in the Words of their Contemporaries; David Ross, Scotland: History of a Nation; ODNB.com; Tracy Borman, The Private Lives of the Tudors; Sarah Gristwood, The Tudors in Love: The Courtly Code Behind the Last Medieval Dynasty; John Cannon, editor, The Oxford Companion to British History; Arthur D. Innes, A History of England Under the Tudors; J.D. Mackie, The Earlier Tudors 1485-1558.
*
My Books
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online bookshop.
OUT NOW! Heroines of the Tudor World
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. These are the women who made a difference, who influenced countries, kings and the Reformation. In the era dominated by the Renaissance and Reformation, Heroines of the Tudor World examines the threats and challenges faced by the women of the era, and how they overcame them. From writers to regents, from nuns to queens, Heroines of the Tudor World shines the spotlight on the women helped to shape Early Modern Europe.
Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK.
Women of the Anarchy
Two cousins. On the one side is Empress Matilda, or Maud. The sole surviving legitimate child of Henry I, she is fighting for her birthright and that of her children. On the other side is her cousin, Queen Matilda, supporting her husband, King Stephen, and fighting to see her own son inherit the English crown. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how these women, unable to wield a sword, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It show how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other.
Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK.
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon. Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org.
Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell – and Tony Riches. We discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online bookshop.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter and Instagram.
*
©2024 Sharon Bennett Connolly FRHistS