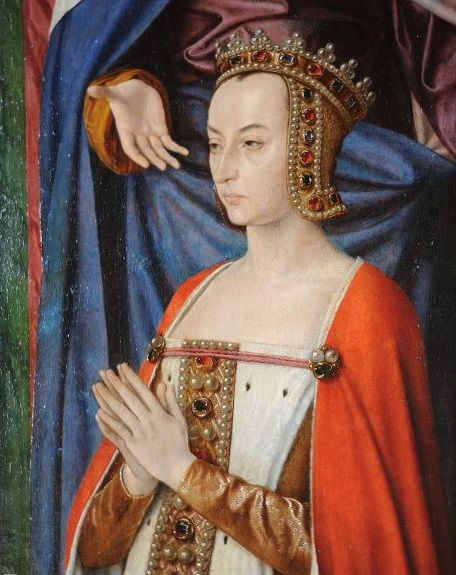
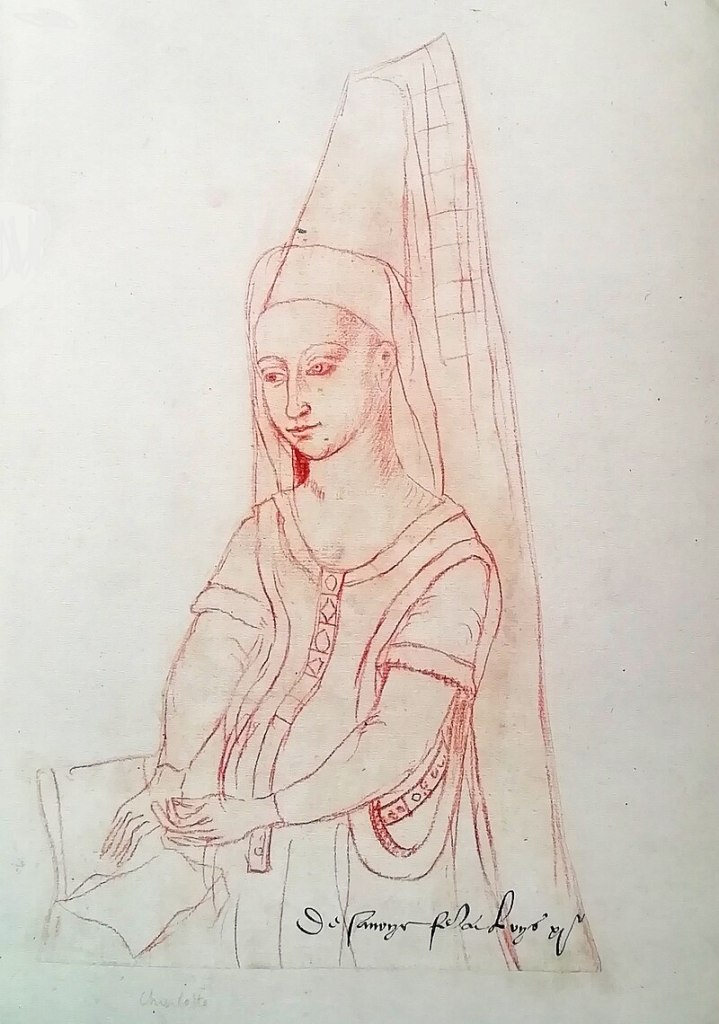
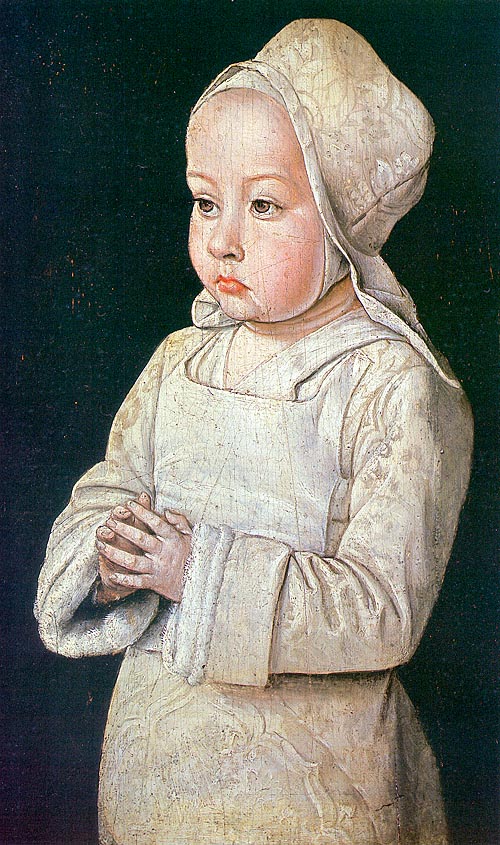
Anne de France, also known as Anne de Beaujeu, crosses the invisible divide between the medieval and Tudor eras. As with many rulers from medieval times, Anne was called upon to act as regent for an underage king. She was regent of France during the minority of her younger brother, Charles VIII. Anne was the third child born to Louis XI of France and his second wife, Charlotte of Savoy, but she was the first to survive infancy. Louis’ first wife, Margaret of Scotland, was a daughter of James I and Joan Beaufort and had died in August1445, aged 20.
Anne was born at Genappe, near Brussels, in April 1461. At the time of her birth her father was still dauphin of France. However, just a few months later, Anne’s grandfather, Charles VII, the man who had attained the crown thanks to the efforts of Joan of Arc, died.
The unfortunate king had had a fractious relationship with his son and heir, Louis; they did not see each other for the last fifteen years of Charles VII’s life. Louis plotted intrigue with his neighbours and had even raised an army against his father in 1455, following arguments over Louis’ marriage to Charlotte. He eventually fled to Burgundy with his wife after his father threatened to invade his lands in the Dauphiné. He refused to return to France, despite being told that his father was dying; Louis waited at the French border for news that he was king. Charles VII died of starvation on 22 July 1461, after a tumour in his jaw prevented him from eating, and Louis immediately returned to France for his coronation.
Louis XI was thirty-eight years old when he became king. He was not a likable man. He possessed a keen intelligence and few scruples. His main political aim was to expand his kingdom, using whatever methods would achieve this. He was pious and cultivated, in contrast to the ostentation and debauchery of his predecessors. His web of political intrigues often got him into international hot water, such as the adventure of Péronnne in 1468, when Louis incited the people of Liège to revolt against the Duke of Burgundy. Under the pretext of negotiation, Louis was arrested by the Duke and forced to offer him financial aid. However, these initial setbacks did not last. Louis was a wily diplomat, at home and abroad, earning him the nickname ‘the universal spider’. He managed to extend French territory by acquiring the French duchy of Burgundy, Picardy, Anjou, Maine and Provence. Louis relied on men of modest means to run his administration, rightfully anticipating that they would be more dependent on him and his goodwill than wealthy nobles. He encouraged the bourgeoisie and initiated the Grand Conseil. He also increased the number of military companies who came directly under the command of the king rather than his nobles.
On his accession, Louis’ daughter, Anne, was installed in the Chateau at Amboise, away from the court, with her mother Charlotte of Savoy and paternal grandmother, Marie of Anjou. Anne was given her own attendants, including chambermaids, nurses and a cradle-rocker. Her mother was in charge of Anne’s education. The queen had an extensive library, including classical works by authors such as Cicero, romances, psalters, histories and books on government. Anne inherited the books on her mother’s death; they were still in her library at Moulins when she herself died.
While still in the cradle, in fact as soon as her father was on the throne, Anne was the most eligible princess in Europe. Combined with great energy; many thought her the mirror image of her father in her keen political mind, although not in other ways. She was considered as a bride for Edward IV in England, Duke Francis II of Brittany and even her uncle Charles, Duke of Berry. Any age difference did not matter to her father, who offered the four-year-old princess to the thirty-two-year-old Count of Charolais– Charles the Bold, the future Duke of Burgundy. A betrothal to Nicholas, Duke of Lorraine, came to nothing when the duke broke it off to pursue Mary, Duchess of Burgundy. When she was twelve, almost thirteen, Anne’s future was decided when she married Pierre de Bourbon on 3 November 1473. At thirty-four, Pierre was twenty-one years her senior.
Pierre’s brother, the Duke of Bourbon, allowed him to use the courtesy title of Lord of Beaujeu and gave him rule of the Beaujolais. However, the newly married couple resided in the king’s court at Plessis-lès-Tours. For Anne, the next ten years were spent at the court and, particularly, with her father– during which time Louis XI said Anne was ‘the least foolish woman in France, but a wise one there was not’ (‘Elle était la moins folle femme de France, car de sage il n’en était point’). Anne, who would be called ‘Madame La Grande’ had a sharp political intelligence. She had a handsome face but was not considered beautiful. She fell pregnant in 1476, but little is known of the outcome of the pregnancy, it is possible that she had a short-lived son, Charles, Count of Clermont, but the details are sketchy. In 1481, Anne was given the County of Gien by her father to allow her to finance her own household. In April 1483 she was despatched to Hesdin to bring her little brother’s bride, three-year-old Margaret of Austria, to France. The little princess was to be brought up at the French court until she was old enough to marry the thirteen-year-old dauphin, Charles.

Anne was twenty-two years old when Louis XI died aged sixty on 30 August 1483, at Plessis-lès-Tours in the Loire Valley. He was succeeded by his son, Charles VIII, who was thirteen years old. Louis had not provided for a regency – young Charles was ten months short of his majority – although he had intended to set up a regency council, which would include the young king’s mother, Charlotte of Savoy, and Louis, Duke of Orléans. Louis was a great-grandson of Charles V and brother-in-law to the king and his sister, Anne de Beaujeu, being married to Jeanne de France; he was also Charles VIII’s heir until he produced a son of his own.
Anne’s husband Pierre, Lord of Beaujeu, was to be appointed the council’s president. However, Anne and her husband had also been appointed Charles’s guardians and it seemed a natural progression for them to take over the government of the realm. Charles was crowned on 30 May 1484 and, in the same year, to appease the populace, an Estates General was called. The body which brought together representatives from the Three Estates (nobility, clergy and commons) had last met in 1439. Their grievances, such as requests for reductions in the tailles and no taxation without the consent of the Estates, were heard and promises made; and the representatives went home content they had been listened to, even though their demands were not entirely met.
The nobility, who had control of the army, and Louis d’Orléans in particular, were not happy with the arrangements. Encouraged by Archduke Maximilian of Austria and Duke Francis of Brittany, Louis and his supporters took up arms in what became known as ‘the mad war’ or ‘the silly war’. They were soundly defeated, their army crushed at Saint-Aubin-du-Cormier in July 1488, and the Duke of Orléans taken prisoner.
Anne’s greatest success was in Brittany, a semi-autonomous duchy within France. The Duke of Brittany, Francis, died in 1488 leaving his thirteen-year-old daughter Anne as his sole heir. Before his death, in an attempt to keep Brittany from being swallowed up by the French crown, the Duke offered his daughter’s hand in marriage to Maximilian of Austria. However, Maximilian was too far away to protect the duchy when the French army invaded. Anne of Brittany was forced to agree to marry Charles VIII, although Brittany would remain in Anne’s hands. This move eventually led to the annexation of Brittany by the crown. No longer needed as a bride, little Margaret of Austria was sent home and Charles VIII married Anne of Brittany on 6 December 1491. The marriage treaty had one unusual clause in that should Charles die before they had children, Anne was to marry Charles’s heir, the next king of France.
This diplomatic coup was one of the last of the Beaujeu regency as Charles VIII was now twenty and of an age and desire to rule. In 1488, Anne de Beaujeu had become Duchess of Bourbon following the death of Pierre’s older brother, John; the title had initially passed to another older brother, Charles, an Archbishop, who was persuaded to relinquish it after holding it for just two weeks, following Pierre’s invasion of the duchy. Anne and Pierre, now the Duke and Duchess of Bourbon, had become the richest, most powerful nobles in the realm. Although she still acted as an advisor to her young brother, Anne de Beaujeu now turned her attention to her new duchy, familiarising herself with her lands and its administration. She started a building programme, which included the rebuilding of the ducal castle at Gien, and the palace at Moulins. She also reorganised the duchy’s administration, codified its laws and raised taxes. Theirs was the epitome of a Renaissance court, the couple being patrons of the arts and literature. Anne particularly loved paintings, tapestries and books.
Anne finally gave birth to a surviving child, a daughter, on 10 May 1491, who was named Suzanne. Suzanne was carefully educated by her mother, who wrote a book, Les Enseignements d’Anne de France, Duchesse de Bourbonnais et d’Auvergne, à sa fille Suzanne de Bourbon, giving advice to her daughter on the proper behaviour expected of a noblewoman. Anne de Beaujeu was made regent again in 1494, when her brother Charles VIII led his army into Italy. She financially supported the king’s campaign by loaning him 10,000 livres; she made him pay it back in instalments and had recovered the full amount within a year. Charles died in 1498 after striking his head on a door lintel, leaving no direct heir. His distant cousin Louis, Duke of Orléans, succeeded him as King Louis XII. He immediately applied to the papacy for an annulment of his marriage to Anne de Beaujeu’s sister, Jeanne, in order to marry the dowager queen, Anne of Brittany, as the terms of her original marriage contract dictated. In return for Anne de Beaujeu’s support of his accession and repudiation of her sister, Louis agreed to waive royal rights to the duchy of Bourbon and the Auvergne and to allow these rights to pass to Suzanne, should Anne produce no male heir.
In 1503, Pierre de Beaujeu, Duke of Bourbon, fell ill while returning home to Moulins from the French court. He succumbed to a fever, which attacked his body for two months before he died on 10 October. Pierre arranged for Suzanne to marry a prince of royal blood, Charles d’Alençon, and called him to Moulins so the wedding could take place before his death. However, Charles arrived too late and could only act as chief mourner at Pierre’s funeral, rather than as bridegroom to Suzanne. Suzanne’s mother then broke the marriage contract and Suzanne would marry her cousin, Charles III of Bourbon Montpensier, Constable of France, but she died in 1521, childless.
Anne de Beaujeu, Duchess of Bourbon, died on 14 November 1522 at the Château of Chandelle, Coulandon. She was buried alongside her husband and daughter in the abbey at Sauvigny. Her lands and personal title, at her own request, passed to her son-in-law, Charles of Bourbon-Montpensier.
Anne de Beaujeu was regent of France at a time when the country was transitioning from the medieval to the early modern era. She successfully steered the country through civil unrest and initiated the merging of Brittany into the French crown, which would be definitively sealed in 1532.
*
Images:
Courtesy of Wikipedia except the ‘Les Enseignements‘ which is ©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly
Sources:
Pierre Goubert, The Course of French History; Les Enseignements d’Anne de France, Duchesse de Bourbonnais et d’Auvergene, à sa fille Suzanne de Bourbon (‘The lessons of Anne of France, Duchess of Bourbon and Auvergne, to her daughter Suzanne of Bourbon’); Abernethy, Susan, ‘Anne de Beaujeu, Duchess of Bourbon and Regent of France’ (article);
*
My Books:
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
Out now: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
‘Scotland’s Medieval Queens gives a thorough grounding in the history of the women who ruled Scotland at the side of its kings, often in the shadows, but just as interesting in their lives beyond the spotlight. It’s not a subject that has been widely covered, and Sharon is a pioneer in bringing that information into accessible history.’ Elizabeth Chadwick (New York Times bestselling author)
Available now from Amazon and Pen and Sword Books
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. Heroines of the Tudor World is now available from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon.
Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org. Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell and Michael Jecks, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved.
Every episode is also now available on YouTube.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads, Bluesky and Instagram.
*
©2025 Sharon Bennett Connolly FRHistS