It is time for me to get back to some serious book reviewing. So, in order to catch up, I thought I’d do two reviews in one post. Both books are from the Tudor period and look into the heirs to the Tudor throne, and the impact of Henry VIII’s actions on those children. Each books provide a fascinating insight into the lives of prominent Tudors and shows a side of Henry VIII that is often overlooked.
Henry VIII’s Children by Caroline Angus
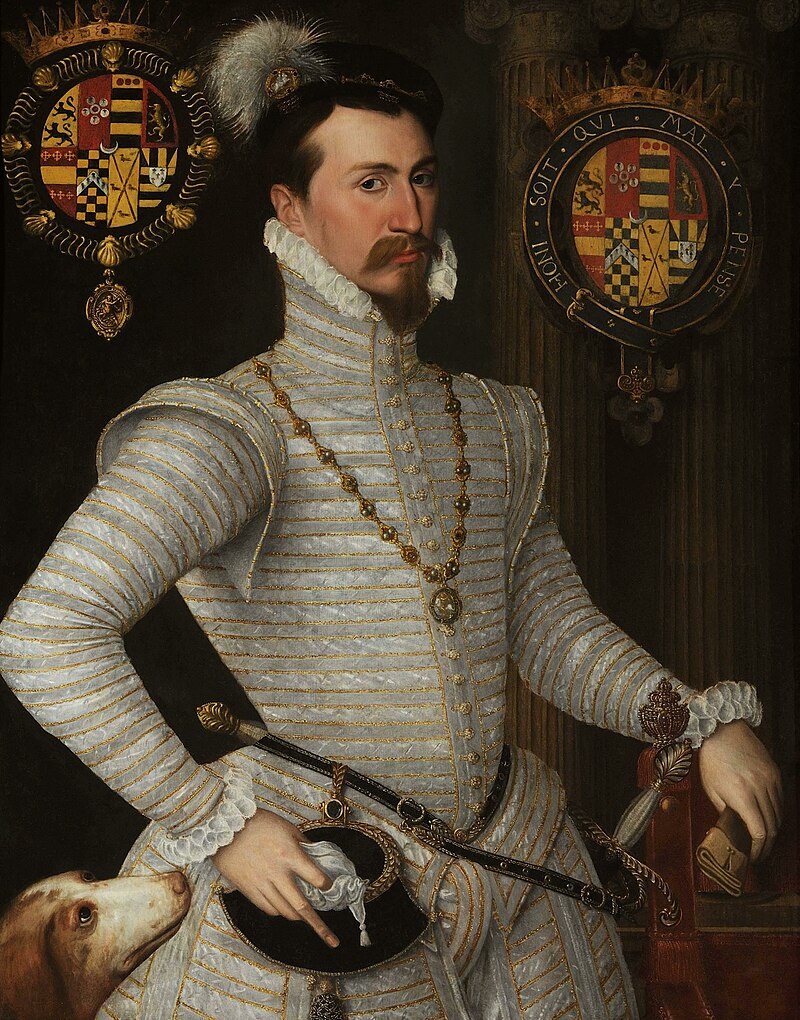
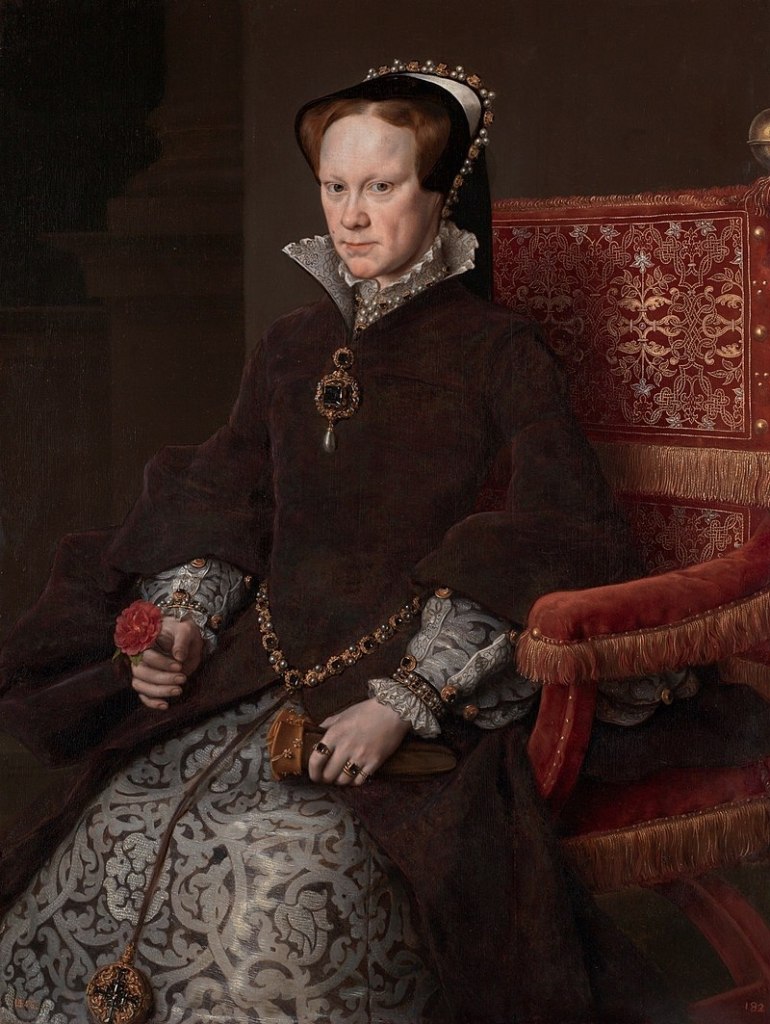
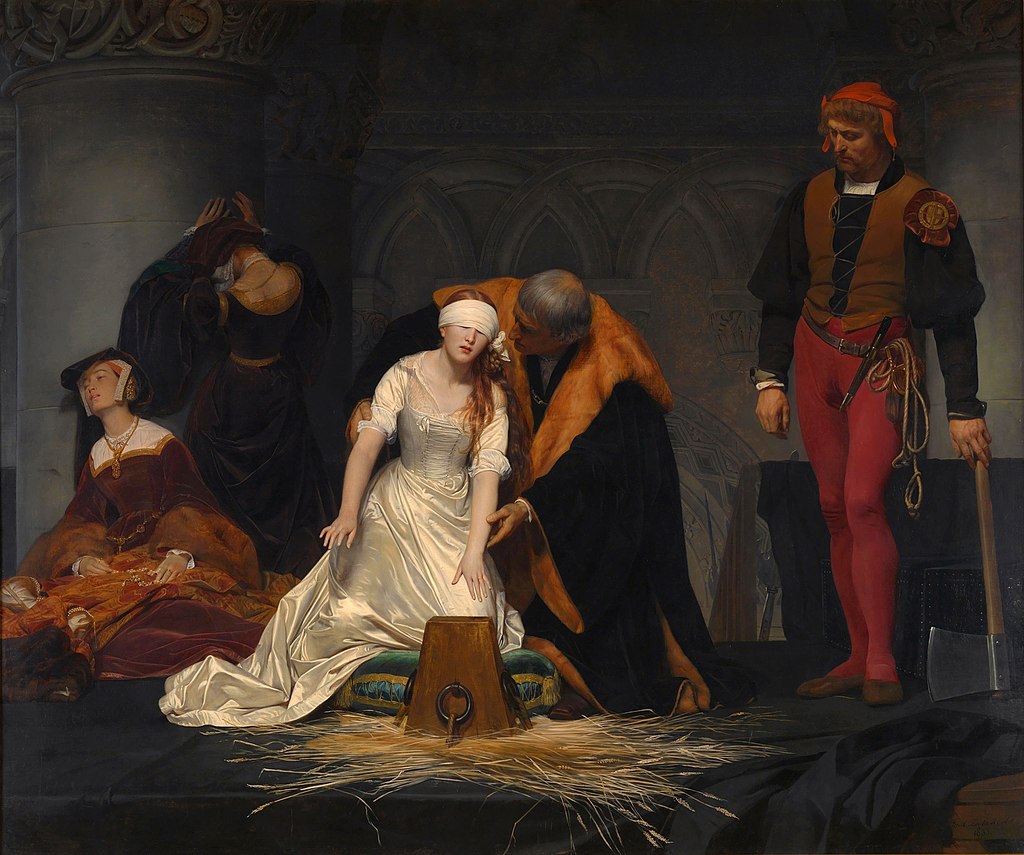
Of the five Tudor monarchs, only one was ever born to rule. While much of King Henry VIII’s reign is centred on his reckless marriage choices, it was the foundations laid by Henry and Queen Katherine of Aragon that shaped the future of the crown. Among the suffering of five lost heirs, the royal couple placed all their hopes in the surviving Princess Mary. Her early life weaves a tale of promise, diplomacy, and pageantry never again seen in King Henry’s life, but a deep-rooted desire for a son, a legacy of his own scattered childhood, pushed Henry VIII to smother Mary’s chance to rule. An affair soon produced an unlikely heir in Henry Fitzroy, and while one child was pure royalty, the other illegitimate, the comparison of their childhoods would show a race to throne closer than many wished to admit.
King Henry’s cruelty saw his heirs’ fates pivot as wives came and went, and the birth Princess Elizabeth, saw long-term plans upended for short-term desires. With the death of one heir hidden from view, the birth of Prince Edward finally gave the realm an heir born to rule, but King Henry’s personal desires and paranoia left his heirs facing constant uncertainty for another decade until his death. Behind the narrative of Henry VIII’s wives, wars, reformation and ruthlessness, there were children, living lives of education among people who cared for them, surrounded by items in generous locations which symbolised their place in their father’s heart. They faced excitement, struggles, and isolation which would shape their own reigns. From the heights of a surviving princess destined and decreed to influence Europe, to illegitimate children scattered to the winds of fortune, the childhoods of Henry VIII’s heirs is one of ambition, destiny, heartache, and triumph.
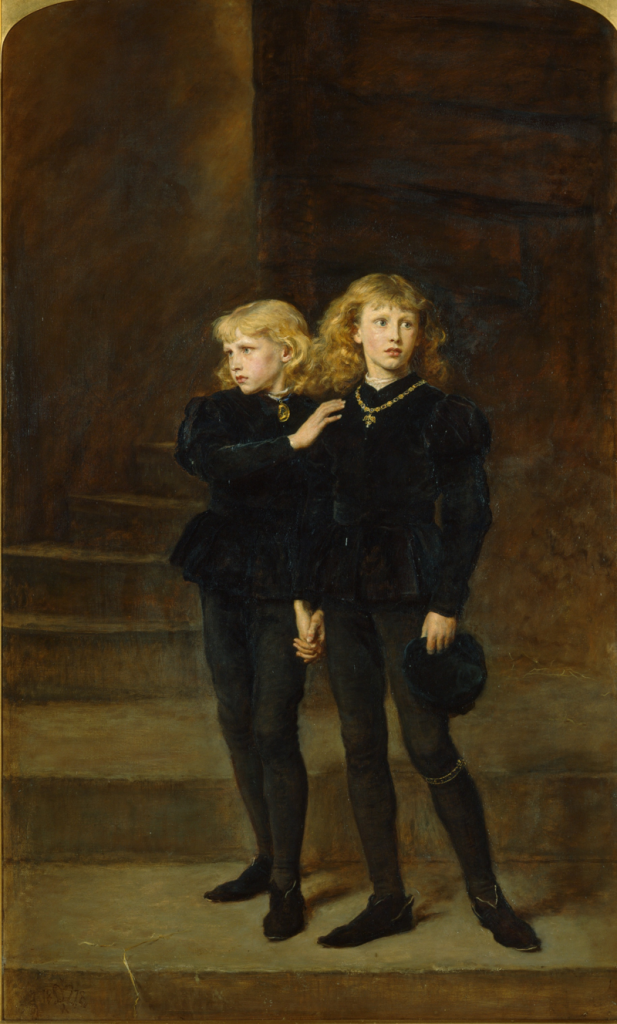
Henry VIII left a long shadow, especially for his children. Caroline Angus looks into the lives and experiences of Henry’s 3 legitimate children, Edward VI, Mary I and Elizabeth I, alongside his only recognised illegitimate child, Henry Fitzroy, Duke of Richmond. And the other possible candidates to be Henry’s offspring, including Catherine Carey.
Henry VIII’s Children is a very easy and enjoyable read. You get absorbed into Caroline Angus’s love of her subject. Her research is thorough and all her arguments are supported by evidence. Where there is conjecture, the author presents both sides and lets the reader find their own conclusion, while presenting what she thinks most likely. I did not agree with all her conclusions, particularly when it comes to Catherine Carey – I am not convinced she was Henry VIII’s daughter, not that Henry’s relationship with Mary Boleyn lasted as long as some historians suggest. I just don’t think we have enough information. But it was interesting to read Caroline’s thoughts on the subject and see how she came to her conclusions.
It certainly gave me food for thought!
The Tudors are always a fascinating subject and Caroline Angus does a wonderful job of igniting the reader’s passion in her subject.
The strength of Henry VIII’s Children lies in its fascinating investigation into the lives of Henry’s 3 ‘legitimate’ children and how their fates were manipulated and directed by Henry’s obsession for a male heir, and his multiple marriages. Poor Mary I had 5 stepmothers! just imagine how she must have felt, watching her mother shunned and sidelined by the father she adored, not being allowed to visit her on her deathbed, nor being allowed to receive her mother’s comfort when she was ill and scared. The mind games Henry VIII played with his eldest child, in order to get her acquiescence, are something to behold.
And then there’s poor Elizabeth, her mother executed before her 3rd birthday, and yet she is the one who surpassed all Henry’s dreams for his children. Elizabeth is the one who had a golden age named after her. She is also the one who always lived in the shadow of her mother’s fate. Caroline Angus looks into all aspects of Elizabeth’s life, especially the childhood and adolescence that shaped her future.
And Edward! the golden boy. The heir who was so desired that his father broke with Rome to get. A boy who was the hope of a nation but died so tragically young.
Caroline Angus looks at them all with such enthusiasm and animation that they jump off the page.
An eminently readable nook that I have no hesitation in recommending.
To Buy Henry VIII’s Children
About the Author:
Caroline Angus is a New Zealand-based author raising four sons. Caroline studied history at Universitat de València, Spain, spending ten years dedicated to the Spanish Civil War and the resulting dictatorship. Caroline went on to study with King’s College London, specialising in Shakespeare and British royal history. After a decade of writing fiction, including the Secrets of Spain series, focusing on the lives of Valencian interviewees between 1939 and 1975, and the more recent Queenmaker Trilogy, eleven years of Thomas Cromwell and his fictional attendant Nicòla Frescobaldi, Caroline is now creating non-fiction works on the surviving papers of Thomas Cromwell.
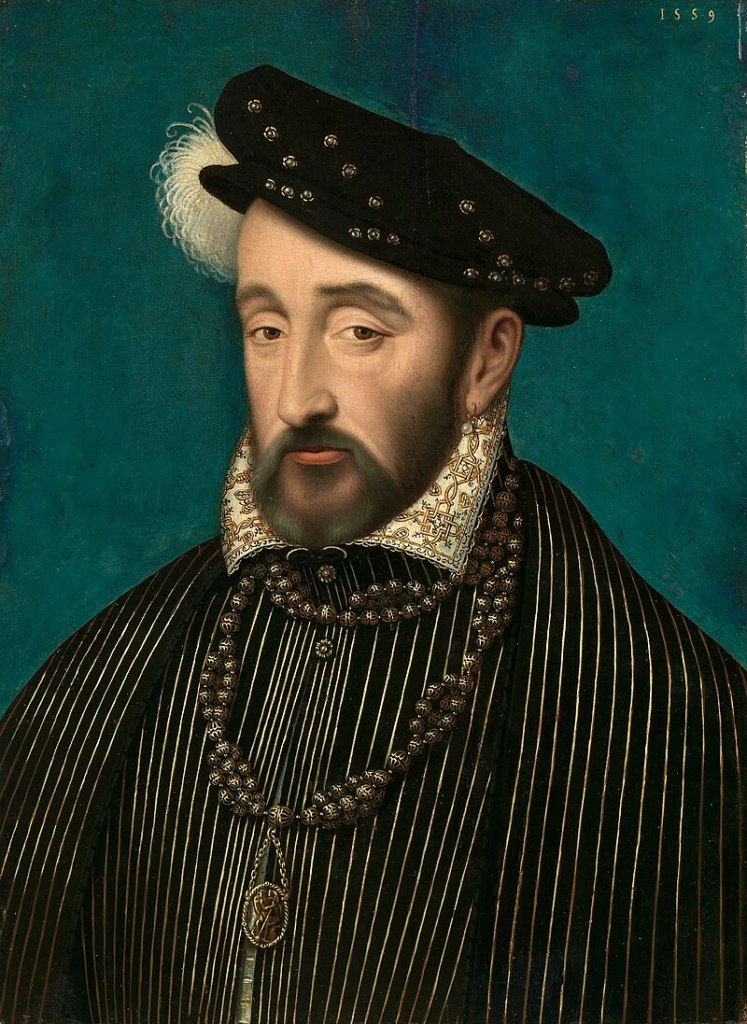
Henry VIII’s True Daughter by Wendy J Dunn
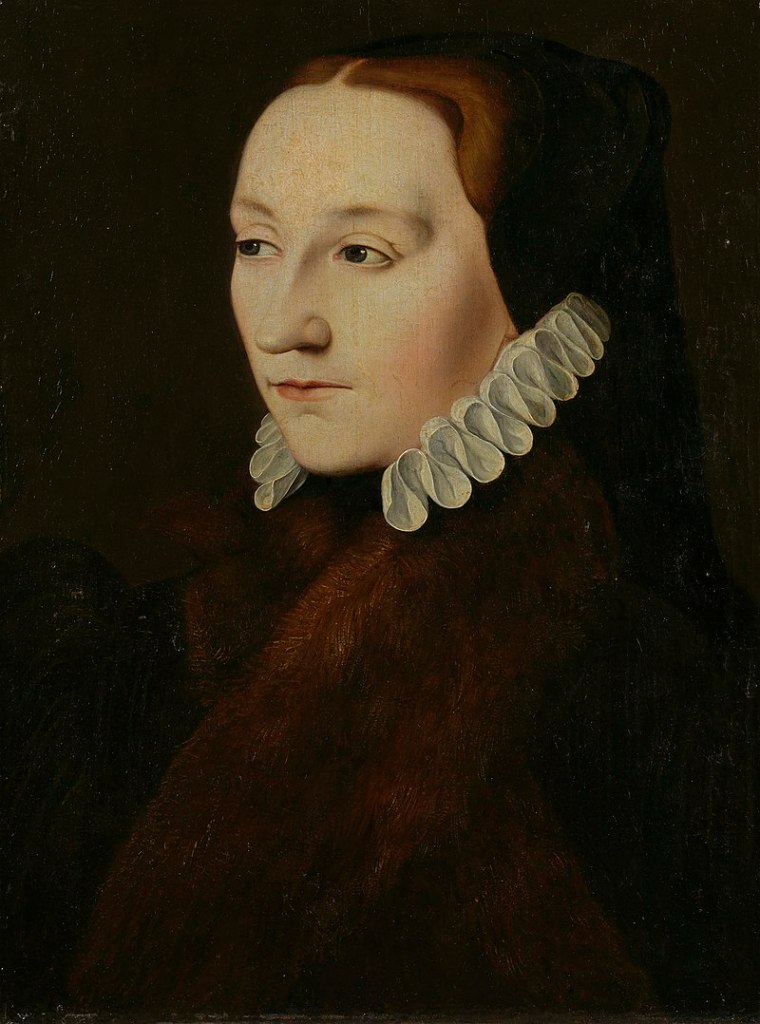
The lives of Tudor women often offer faint but fascinating footnotes on the pages of history. The life of Catherine – or Katryn as her husband would one day pen her name – Carey, the daughter of Mary Boleyn and, as the weight of evidence suggests, Henry VIII, is one of those footnotes.
As the possible daughter of Henry VIII, the niece of Anne Boleyn and the favourite of Elizabeth I, Catherine’s life offers us a unique perspective on the reigns of Henry and his children. In this book, Wendy J. Dunn takes these brief details of Catherine’s life and turns them into a rich account of a woman who deserves her story told. Following the faint trail provided of her life from her earliest years to her death in service to Queen Elizabeth, Dunn examines the evidence of Catherine’s parentage and views her world through the lens of her relationship with the royal family she served.
This book presents an important story of a woman who saw and experienced much tragedy and political turmoil during the reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI, and Mary I – all of which prepared her to take on the vital role of one of Elizabeth I closest and most trusted women. It also prepared her to become the wife of one of Elizabeth’s privy councillors – a man also trusted and relied on by the queen. Catherine served Elizabeth during the uncertain and challenging first years of her reign, a time when there was a question mark over whether she would succeed as queen regnant after the failures of England’s first crowned regnant, her sister Mary.
Through immense research and placing her in the context of her period, HENRY VIII’S TRUE DAUGHTER: CATHERINE CAREY, A TUDOR LIFE draws Catherine out of the shadows of history to take her true place as the daughter of Henry VIII and shows how vital women like Catherine were to Elizabeth and the ultimate victory of her reign.
Henry VIII’s True Daughter: Catherine Carey, A Tudor Life by Wendy J. Dunn is a perfect accompaniment to Henry VIII’s Children. Focusing on the eldest child of Mary Boleyn and William Carey, Wendy J. Dunn investigates Catherine’s origins and the stories around her conception and birth – in particular, her mother’s relationship with Henry VIII. It has long been thought possible that Catherine was Henry’s daughter and that Mary Boleyn’s marriage to William Carey was arranged to conceal the king’s affair. Henry himself admitted he had slept with Mary Boleyn when he was once accused of sleeping with Anne Boleyn’s mother, replying along the lines of ‘the sister but never the mother.’
So, we know they had a relationship, but how long it lasted and whether Catherine was the result of that relationship is still uncertain. Wendy attempts to lift away that uncertainty and presents all the evidence and conjecture that has been gather over the years to give us her own conclusions.
But this book is so much more! Henry VIII’s True Daughter gives us insights into the life of a prominent Tudor woman. Whether or not she was the daughter of Henry VIII, she was still at the heart of the Tudor court, especially in the reign of her sister/cousin, Elizabeth I. Catherine was one of Elizabeth’s favourites and was loyal to the queen to the very end of her life. Wendy gives stunning insight into Catherine’s life and career, as well as her marriage and family.
Even if I don’t necessarily agree with all its conclusion, Henry VIII’s True Daughter by Wendy J Dunn is a wonderful, engaging book, giving the reader ample food for thought in her theories and explanations of the life and origins of Catherine Carey. It is a must-read for any fan of Tudor history.
To Buy Henry VIII’s True Daughter
About the Author:
Wendy J. Dunn is an award-winning Australian writer fascinated by Tudor history – so much so she was not surprised to discover a family connection to the Tudors, not long after the publication of her first Anne Boleyn novel, which narrated the Anne Boleyn story through the eyes of Sir Thomas Wyatt, the elder. Her family tree reveals the intriguing fact that one of her ancestral families – possibly over three generations – had purchased land from both the Boleyn and Wyatt families to build up their holdings. It seems very likely Wendy’s ancestors knew the Wyatts and Boleyns personally. Wendy is married, the mother of four adult children and the grandmother of two amazing small boys. She gained her PhD in 2014 and loves walking in the footsteps of the historical people she gives voice to in her books. Wendy also tutors writing at Swinburne University of Technology, Australia. HENRY VIII’S TRUE DAUGHTER: CATHERINE CAREY, A TUDOR LIFE is her first full-length nonfiction work.
*
My Books:
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
OUT NOW! Heroines of the Tudor World
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. These are the women who made a difference, who influenced countries, kings and the Reformation. In the era dominated by the Renaissance and Reformation, Heroines of the Tudor World examines the threats and challenges faced by the women of the era, and how they overcame them. From writers to regents, from nuns to queens, Heroines of the Tudor World shines the spotlight on the women helped to shape Early Modern Europe.
Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK.
Coming 30 January 2025: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
Available for pre-order now.
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon. Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org.
Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads and Instagram.
*
©2024 Sharon Bennett Connolly FRHistS.