Today it is a pleasure to welcome my good friend, Kasia Ogrodnik to History…the Interesting Bits with a little bit of Polish history for us. I have been wanting to tell the story of King Jadwiga since writing about her in Heroines of the Medieval World. But Kasia is far better qualified to write about her compatriot, Poland’s famous female king and saint, and Jadwiga’s influential female relatives.
So, over to Kasia…
Empresses, Saints and Female-Kings: The Four Great-Granddaughters of King Ladislaus the Elbow-High

The night of 19 May 1365 saw a young girl leaving Pisa on horseback. With her hair loose, clad only in her nightgown she was galloping to safety after fire broke out in Palazzo degli Anziani. Judging by her looks no one would have guessed this girl was in fact Holy Roman Empress and Queen of Bohemia.
Anna of Schweidnitz, Silesia (today Poland), was the only child of Duke Henry II, the grandson of King Ladislaus the Elbow-High of Cracow (Poland). Upon her father’s death she was placed under the care of his elder brother, her uncle, Bolko II the Small. The ruler of the small, but politically important duchy, Bolko was the last independent Silesian Piast. Since Charles IV of Luxembourg intended to annex the entirety of Silesia to the Kingdom of Bohemia, Bolko’s duchy, being the only missing part, was crucial to his plans. To secure the Schweidnitz inheritance Charles married Anna and this is how her journey began. Of course, she was not the only great-granddaughter of King Ladislaus to make an illustrious career. His three other great-granddaughters were to leave their marks on the world, too, and indelible ones. Two of them were to be crowned ”kings” and one proclaimed saint.
Anna of Schweidnitz (b.1339), Queen of Bohemia and Holy Roman Empress, was Charles IV of Luxembourg’s third wife. Initially she was betrothed to his son, Wenceslaus, but the boy died while still very young. His mother, Charles’s second wife died too shortly afterwards. To secure the Schweidnitz succession Charles decided to marry his late son’s fiancee himself. Anna was raised and educated at the splendid court of Queen Elizabeth of Poland (her late father’s aunt) at Buda, where she was sent by her uncle and official guardian, Duke Bolko II the Small. It was there where she and Charles were married in the closing days of May 1353. Shortly afterwards the newlyweds returned to Prague and paid a visit to Schweidnitz, where the succession treaty was signed according to which the duchy was to be inherited by Anna and her children by Charles upon the death of her uncle Bolko and his wife Agnes of Habsburg. On 28 July 1353, Anna was crowned Queen of Bohemia and the following year, on 9 February 1354, Queen of Germany. The year 1355 saw the royal couple in Italy, where on Easter Sunday (5 April 1355) they were crowned Holy Roman Emperor and Holy Roman Empress in a splendid ceremony in the Basilica of Saint Peter, Rome.
Anna and Charles’s first child, a daughter, Elizabeth, was born in 1358. Charles was overjoyed, but Anna felt she failed her husband (which we know thanks to her surviving correspondence with Petrarch). A much awaited son and heir arrived three years later, named Wenceslaus, traditional name of the rulers of Bohemia. He was to become Charles’ beloved and favoured child. Anna died on 11 July 1362, in childbirth, aged 23. The child did not survive, either, and they were buried together in St Vitus Cathedral, Prague. Anna was remembered for her personal charm and sweet nature. Not only did she receive a bluestocking education, but she was also considered one of the style icons of her time, her reputation as a great beauty resting on the surviving images created during her lifetime and shortly after her untimely death. Tradition has it that of Charles’ four wives it was Anna he loved most. Stricken with grief upon her passing, he did not remarry until a political situation forced him to. His fourth wife was Anna’s kin, Elizabeth of Pomerania, also great-granddaughter of King Ladislaus the Elbow-High.
Elizabeth of Pomerania (Eliška Pomořanská, Elżbieta Pomorska)
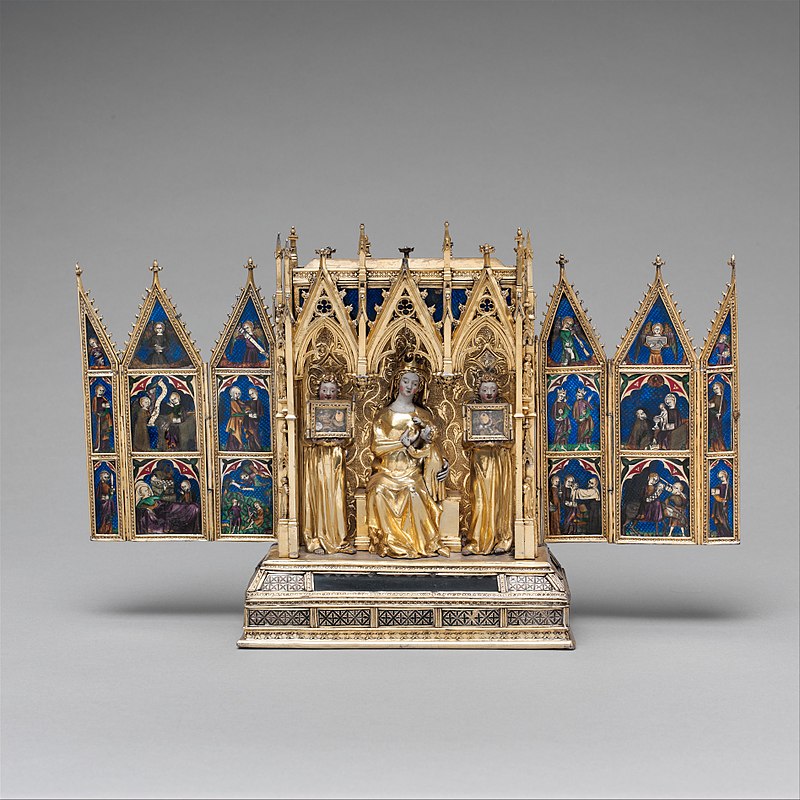

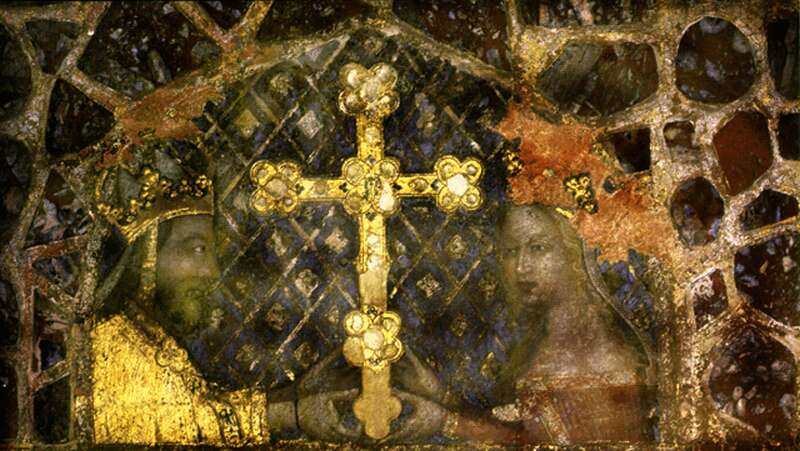
Reliquary Shrine of Elizabeth of Poland, Queen of Hungary, Maria and Jadwiga’s paternal grandmother, attributed to Jean de Touyl, ca. 1350 . Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York
Elizabeth was a daughter of Duke Bogusław the Great of Pomerania and Princess Elżbieta of Poland. In 1362 her maternal grandfather, King Casimir the Great of Poland together with his nephew, Louis the Great of Hungary, dukes of Austria and Bavaria formed a coalition against Charles IV of Luxembourg. The opposing parties found themselves on the verge of war, which did not break out, however, perhaps due to Anne of Schweidnitz’s untimely death. The rulers came to terms instead and a marriage was forged to consolidate their agreement. Charles was to marry Elizabeth. He was thrice her age, shorter than her and not very attractive. She was described as beautiful, full of life, and as fit as a fiddle. Stories had it that she could break horseshoes with her own hands. She was an avid horse rider and hunter.
The wedding ceremony was celebrated in Kraków on 21 May 1363. Afterwards the couple travelled together to Prague where Elizabeth was crowned Queen of Bohemia. Five years later her imperial coronation at Rome followed. Despite the age difference she and Charles got along well, being married for fifteen years. Their union produced six children, four of whom were to reach adulthood. Charles and Elizabeth’s eldest child, a daughter Anne, was to marry Richard II and become Queen Consort of England. Their son, Sigismund was to be crowned King of Bohemia, Hungary and Holy Roman Emperor. Charles IV died in 1378. Elizabeth herself was to outlive her husband for fifteen years. She died in 1393 and like his three wives before her, she was buried in St Vitus Cathedral, Prague.
Mária [Mary] of Anjou, King of Hungary
Mary was one of the three daughters of Louis the Great of Hungary and his second wife, Elizabeth of Bosnia. In 1379, Mary’s elder sister Catherine died, leaving her and her sister Jadwiga Louis’s sole surviving children. The matter of Polish succession had been on the agenda long before Mary was born. Upon King Casimir the Great’s death in 1370 his nephew, Mary’s father, Louis was crowned king of Poland. Initially it was Mary, who was to succeed him as the king of Poland, but the events took a different turn, and in the end she was replaced by her younger sister, Jadwiga [Hedwig].
Mary was crowned “king” of Hungary on 17 September 1382, seven days after her father’s death. However, the idea of a female monarch was not popular among the Hungarian nobility. Many nobles considered Charles III of Naples, Mary’s distant cousin, the lawful heir.
Charles landed in Dalmatia in September 1385. In October Mary was married to Sigismund of Luxembourg, however, this could not prevent Charles from entering the capital. Mary was forced to renounce the throne and Charles’s coronation took place on 31 December 1385. He did not rule for long. Two months later, in February 1386, he was murdered, most probably at the instigation of Mary’s mother. Mary was restored, but in July she and her mother were captured by the dead king’s supporters. Famed for her beauty, but not for her political decisions, Mary’s mother met a violent end. After imprisonment by her opponents in Novigrad castle, she was found guilty of the murder of Charles III of Naples and strangled to death before her daughter’s own eyes, her body put on display, hanging on a rope from the castle walls. Mary survived and was rescued by her husband, Sigismund, who was crowned king of Hungary afterwards. Mary officially remained his co-ruler, but had no real influence on the government. She died on 17 May 1395 after falling from a horse during a hunting accident. She was pregnant at the time. Her prematurely born son did not survive either.
Jadwiga [Hedwig] of Anjou, king and patron saint of Poland

Mary’s younger sister, Hedwig was born on 18 February 1374, being the youngest of the three daughters of Louis the Great of Hungary and Elizabeth of Bosnia.
Both Mary and Jadwiga received a bluestocking education, Jadwiga both at the cultivated court of Hungary and in Vienna, at the court of her future father-in-law. Not only could Jadwiga read and write, but she also spoke fluent Latin and German. As the king of Poland she owned a big library and always showed an active and generous support of scholars and learning institutions.
Since Polish nobles did not like the idea of Mary’s consort, Sigismund of Bohemia, becoming de facto their king, they appealed to Elizabeth of Bosnia, the dowager queen, who had assumed regency, asking to send the younger of her two surviving daughters to Kraków. Elizabeth agreed and absolved the Polish nobles from the oath of loyalty they had pledged to Mary.
Jadwiga’s coronation took place on 16 October 1384 in Wawel Cathedral, Kraków, where she was crowned ”king” of Poland. On 18 January 1385 the Lithuanian delegation came to the capital and a meeting was held with the representatives of the Polish nobility. Jadwiga was to marry the ruler of pagan Lithuania, Jogaila. In the opening days of 1386, Jadwiga publicly called off her engagement to Wilhelm Habsburg and married newly baptised Jogaila, who was to come down in history under his new name, Władysław Jagiełło [Ladislaus Jagiellon]. At the time of their wedding she was twelve, he was thirty-five. Władyslaw was crowned king on 4 March 1386.
Despite her young age Jadwiga continued to play an active role in the administration and politics of her realm. She conducted the negotiations with the knights of the Teutonic Order, but also on the Hungarian front. Jadwiga conferred with her sister Mary on numerous occasions. Their meetings were held both in Hungary and in Lesser Poland. She also intervened in Lithuania, where she peacefully resolved dynastic disputes between the ruling fractions.

She was famed for her charity and showing great care to the poor and the ill. Her active and generous support of scholars and learning institutions did not waver over the years. In her last will she donated all her jewelry, her rich dresses and other valuable objects to the Kraków Academy (the first Polish university founded by Kazimierz Wielki), now the Jagiellonian University. Additionally, she founded a dormitory for Polish students at the University of Prague.
Jadwiga died from complications in childbirth on 17 July 1399. She was twenty-five at the time. Her daughter did not survive, either. Almost immediately after her death, Jadwiga’s tomb became the focus of miracles and the destination of pilgrimages. Her cult flourished, with her canonization first mentioned during the funeral ceremony. However, it was to take seven centuries before she was actually canonised by Pope John Paul II. Ever since she has been recognised as patron saint of Poland and considered Polish national hero.
About the author:
Katarzyna Ogrodnik-Fujcik specializes in British literature and history, her area of expertise being the first Plantagenets (the Angevins). She lives in Poland. She writes for different magazines and websites on Polish and European Middle Ages. She runs a blog dedicated to Henry the Young King. She consulted a BBC documentary on William Marshal.
*
My Books:
Signed, dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
OUT NOW! Heroines of the Tudor World
Heroines of the Tudor World tells the stories of the most remarkable women from European history in the time of the Tudor dynasty, 1485-1603. These are the women who ruled, the women who founded dynasties, the women who fought for religious freedom, their families and love. These are the women who made a difference, who influenced countries, kings and the Reformation. In the era dominated by the Renaissance and Reformation, Heroines of the Tudor World examines the threats and challenges faced by the women of the era, and how they overcame them. From writers to regents, from nuns to queens, Heroines of the Tudor World shines the spotlight on the women helped to shape Early Modern Europe.
Heroines of the Tudor World is now available for pre-order from Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK.
Coming 30 January 2025: Scotland’s Medieval Queens
Scotland’s history is dramatic, violent and bloody. Being England’s northern neighbour has never been easy. Scotland’s queens have had to deal with war, murder, imprisonment, political rivalries and open betrayal. They have loved and lost, raised kings and queens, ruled and died for Scotland. From St Margaret, who became one of the patron saints of Scotland, to Elizabeth de Burgh and the dramatic story of the Scottish Wars of Independence, to the love story and tragedy of Joan Beaufort, to Margaret of Denmark and the dawn of the Renaissance, Scotland’s Medieval Queens have seen it all. This is the story of Scotland through their eyes.
Available for pre-order now.
Also by Sharon Bennett Connolly:
Women of the Anarchy demonstrates how Empress Matilda and Matilda of Boulogne, unable to wield a sword themselves, were prime movers in this time of conflict and lawlessness. It shows how their strengths, weaknesses, and personal ambitions swung the fortunes of war one way – and then the other. Available from Bookshop.org, Amberley Publishing and Amazon UK. King John’s Right-Hand Lady: The Story of Nicholaa de la Haye is the story of a truly remarkable lady, the hereditary constable of Lincoln Castle and the first woman in England to be appointed sheriff in her own right. Available from all good bookshops Pen & Sword Books, bookshop.org and Amazon. Defenders of the Norman Crown: The Rise and Fall of the Warenne Earls of Surrey tells the fascinating story of the Warenne dynasty, from its origins in Normandy, through the Conquest, Magna Carta, the wars and marriages that led to its ultimate demise in the reign of Edward III. Available from Pen & Sword Books, Amazon in the UK and US, and Bookshop.org.
Ladies of Magna Carta: Women of Influence in Thirteenth Century England looks into the relationships of the various noble families of the 13th century, and how they were affected by the Barons’ Wars, Magna Carta and its aftermath; the bonds that were formed and those that were broken. It is now available in paperback and hardback from Pen & Sword, Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Heroines of the Medieval World tells the stories of some of the most remarkable women from Medieval history, from Eleanor of Aquitaine to Julian of Norwich. Available now from Amberley Publishing and Amazon, and Bookshop.org. Silk and the Sword: The Women of the Norman Conquest traces the fortunes of the women who had a significant role to play in the momentous events of 1066. Available now from Amazon, Amberley Publishing, and Bookshop.org.
Alternate Endings: An anthology of historical fiction short stories including Long Live the King… which is my take what might have happened had King John not died in October 1216. Available in paperback and kindle from Amazon.
Podcast:
Have a listen to the A Slice of Medieval podcast, which I co-host with Historical fiction novelist Derek Birks. Derek and I welcome guests, such as Bernard Cornwell, and discuss a wide range of topics in medieval history, from significant events to the personalities involved.
*
Don’t forget! Signed and dedicated copies of all my books are available through my online store.
For forthcoming online and in-person talks, please check out my Events Page.
You can be the first to read new articles by clicking the ‘Follow’ button, liking our Facebook page or joining me on Twitter, Threads and Instagram.
*
©2024 Sharon Bennett Connolly FRHistS and Katarzyna Ogrodnik-Fujcik